Genome-wide identification and functional analysis of cupin_1 domain-containing members involved in the responses to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum and abiotic stress in Brassica napus
- PMID: 35979083
- PMCID: PMC9377217
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.983786
Genome-wide identification and functional analysis of cupin_1 domain-containing members involved in the responses to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum and abiotic stress in Brassica napus
Abstract
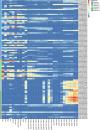
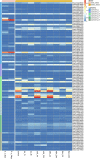
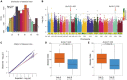
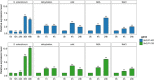
Cupin_1 domain-containing proteins (CDPs) are ubiquitously present in higher plants, which are known to play essential roles in various biological processes. In this study, we carried out genome-wide characterization and systematic investigation of the CDP genes in Brassica napus. A total of 96 BnCDPs, including 71 germin-like proteins (GLPs; proteins with a single cupin_1 domain) and 25 CDP bicupins (proteins with two cupin_1 domains), were identified and clustered into six distinct subfamilies (I-VI) based on the phylogenic analysis, gene structure and motif distribution. Further analysis indicated that whole-genome duplication (WGD) and segmental duplication are main contributors to the species-specific expansion of the BnCDP gene family, and all the duplicated genes subsequently underwent strong purification selection. The promoter region of BnCDPs showed enrichment of cis-regulatory elements associated with development, hormone and stress, as well as transcription factor binding sites, which validates the prediction that BnCDPs are widely involved in plant growth and biotic and abiotic stress responses. The BnCDPs in different subfamilies exhibited obvious differences in expression among 30 developmental tissues/stages of B. napus, implying that BnCDPs may be involved in tissue- and stage-specific developmental processes. Similar trends in expression of most BnCDPs were observed under Sclerotinia sclerotiorum inoculation and four abiotic stresses (dehydration, cold, ABA and salinity), particularly the BnGLPs in subfamily I and III with single cupin_1 domain, revealing that BnCDPs are of great importance in the environmental adaption of B. napus. We then performed a genome-wide association study (GWAS) of 274 B. napus core germplasms on S. sclerotiorum resistance and identified four significantly associated loci harboring five BnGLPs. The expression levels of two candidate genes, BnGLP1.A08 and BnGLP1.C08, were significantly correlated with S. sclerotiorum resistance. Their functional responses to multiple stages of S. sclerotiorum inoculation and four abiotic stresses were further examined through qPCR. Overall, this study provides rich resources for research on the function and evolutionary playground of CDP genes.
Keywords: Brassica napus; GWAS; Sclerotinia sclerotiorum resistance; abiotic stress; cupin_1 domain; germin-like protein.
Copyright © 2022 He, Li, Bai, Xie, Zuo, Liu, Xia, Cheng, Liu, Tong, Zhang and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Members of the germin-like protein family in Brassica napus are candidates for the initiation of an oxidative burst that impedes pathogenesis of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum.J Exp Bot. 2012 Sep;63(15):5507-19. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ers203. Epub 2012 Aug 9. J Exp Bot. 2012. PMID: 22888126 Free PMC article.
-
Genome Structures and Evolution Analysis of Hsp90 Gene Family in Brassica napus Reveal the Possible Roles of Members in Response to Salt Stress and the Infection of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Apr 7;13:854034. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.854034. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35463405 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification of biotin carboxyl carrier subunits of acetyl-CoA carboxylase in Brassica and their role in stress tolerance in oilseed Brassica napus.BMC Genomics. 2022 Oct 17;23(1):707. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08920-y. BMC Genomics. 2022. PMID: 36253756 Free PMC article.
-
Sclerotinia Stem Rot Resistance in Rapeseed: Recent Progress and Future Prospects.J Agric Food Chem. 2021 Mar 17;69(10):2965-2978. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c07351. Epub 2021 Mar 5. J Agric Food Chem. 2021. PMID: 33667087 Review.
-
Phylogenomic analysis of 20S proteasome gene family reveals stress-responsive patterns in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.).Front Plant Sci. 2022 Oct 31;13:1037206. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1037206. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36388569 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Characterization and Potential Function Analysis of the SRS Gene Family in Brassica napus.Genes (Basel). 2023 Jul 10;14(7):1421. doi: 10.3390/genes14071421. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37510325 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of the cupin_1 domain-containing proteins in ma bamboo (Dendrocalamus latiflorus) and their potential role in rhizome sprouting.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Oct 16;14:1260856. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1260856. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37908839 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of Germin-like Protein Family in Response to Seed Germination and Shoot Branching in Brassica napus.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 26;25(21):11518. doi: 10.3390/ijms252111518. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39519071 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

