Drug-induced autoimmune hepatitis: A minireview
- PMID: 35979160
- PMCID: PMC9260871
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i24.2654
Drug-induced autoimmune hepatitis: A minireview
Abstract
Drug-induced autoimmune hepatitis (DIAIH) is a specific phenotype of drug-induced liver injury that may lead to the devastating outcome of acute liver failure requiring liver transplantation. Drugs implicated in DIAIH include antimicrobials such as nitrofurantoin and minocycline, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, statins as well as anti-tumor necrosis agents. The clinical features of drug-induced liver injury are indistinguishable from idiopathic autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) as both may have positive AIH-related autoantibodies, elevated immunoglobulin G, as well as similar histopathological findings. In patients who show no clinical improvement, or there is progressive liver injury despite cessation of the suspected drug, a liver biopsy should be considered, whereby the presence of advance fibrosis on histology favors the diagnosis of idiopathic AIH. Empirical treatment with corticosteroids may be required in patients with non-resolving liver injury. A typical clinical scenario supportive of DIAIH includes a history of drug exposure with spontaneous resolution of liver injury after drug withdrawal and the absence of relapse after rapid steroid taper. In this article we report two cases of DIAIH secondary to Sorafenib and Atorvastatin along with a review of currently available literature. Early identification and treatment often lead to a favorable outcome in DIAIH.
Keywords: Autoimmune hepatitis; Drug-induced autoimmune hepatitis; Drug-induced liver injury; Review.
©The Author(s) 2022. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All authors have no relevant conflict of interest to report.
Figures
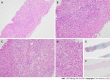
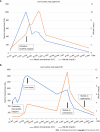
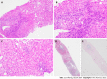
References
-
- Björnsson ES, Bergmann OM, Björnsson HK, Kvaran RB, Olafsson S. Incidence, presentation, and outcomes in patients with drug-induced liver injury in the general population of Iceland. Gastroenterology. 2013;144:1419–1425, 1425.e1. - PubMed
-
- Shen T, Liu Y, Shang J, Xie Q, Li J, Yan M, Xu J, Niu J, Liu J, Watkins PB, Aithal GP, Andrade RJ, Dou X, Yao L, Lv F, Wang Q, Li Y, Zhou X, Zhang Y, Zong P, Wan B, Zou Z, Yang D, Nie Y, Li D, Wang Y, Han X, Zhuang H, Mao Y, Chen C. Incidence and Etiology of Drug-Induced Liver Injury in Mainland China. Gastroenterology. 2019;156:2230–2241.e11. - PubMed
-
- Ostapowicz G, Fontana RJ, Schiødt FV, Larson A, Davern TJ, Han SH, McCashland TM, Shakil AO, Hay JE, Hynan L, Crippin JS, Blei AT, Samuel G, Reisch J, Lee WM U. S. Acute Liver Failure Study Group. Results of a prospective study of acute liver failure at 17 tertiary care centers in the United States. Ann Intern Med. 2002;137:947–954. - PubMed
-
- Wei G, Bergquist A, Broomé U, Lindgren S, Wallerstedt S, Almer S, Sangfelt P, Danielsson A, Sandberg-Gertzén H, Lööf L, Prytz H, Björnsson E. Acute liver failure in Sweden: etiology and outcome. J Intern Med. 2007;262:393–401. - PubMed
-
- Björnsson E, Jerlstad P, Bergqvist A, Olsson R. Fulminant drug-induced hepatic failure leading to death or liver transplantation in Sweden. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2005;40:1095–1101. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

