Downregulation of TNFR2 decreases survival gene expression, promotes apoptosis and affects the cell cycle of gastric cancer cells
- PMID: 35979166
- PMCID: PMC9260869
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i24.2689
Downregulation of TNFR2 decreases survival gene expression, promotes apoptosis and affects the cell cycle of gastric cancer cells
Abstract
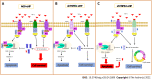
Background: Chronic inflammation due to Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection promotes gastric carcinogenesis. Tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), a key mediator of inflammation, induces cell survival or apoptosis by binding to two receptors (TNFR1 and TNFR2). TNFR1 can induce both survival and apoptosis, while TNFR2 results only in cell survival. The dysregulation of these processes may contribute to carcinogenesis.
Aim: To evaluate the effects of TNFR1 and TNFR2 downregulation in AGS cells treated with H. pylori extract on the TNF-α pathway.
Methods: AGS cell lines containing TNFR1 and TNFR2 receptors downregulated by specific shRNAs and nonsilenced AGS cells were treated with H. pylori extract for 6 h. Subsequently, quantitative polymerase chain reaction with TaqMan® assays was used for the relative quantification of the mRNAs (TNFA, TNFR1, TNFR2, TRADD, TRAF2, CFLIP, NFKB1, NFKB2, CASP8, CASP3) and miRNAs (miR-19a, miR-34a, miR-103a, miR-130a, miR-181c) related to the TNF-α signalling pathway. Flow cytometry was employed for cell cycle analysis and apoptosis assays.
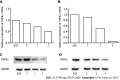
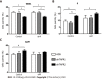
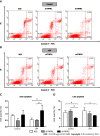
Results: In nonsilenced AGS cells, H. pylori extract treatment increased the expression of genes involved in cell survival and inhibited both apoptosis (NFKB1, NFKB2 and CFLIP) and the TNFR1 receptor. TNFR1 downregulation significantly decreased the expression of the TRADD and CFLIP genes, although no change was observed in the cellular process or miRNA expression. In contrast, TNFR2 downregulation decreased the expression of the TRADD and TRAF2 genes, which are both important downstream mediators of the TNFR1-mediated pathway, as well as that of the NFKB1 and CFLIP genes, while upregulating the expression of miR-19a and miR-34a. Consequently, a reduction in the number of cells in the G0/G1 phase and an increase in the number of cells in the S phase were observed, as well as the promotion of early apoptosis.
Conclusion: Our findings mainly highlight the important role of TNFR2 in the TNF-α pathway in gastric cancer, indicating that silencing it can reduce the expression of survival and anti-apoptotic genes.
Keywords: Gastric cancer; Helicobacter pylori; TNFR1; TNFR2; Tumour necrosis factor-α signalling pathway; miRNAs.
©The Author(s) 2022. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- International Agency for Research on Cancer. Cancer Today fact Sheets, 2018. [cited 11 January 2022]. Available from http://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/cancers/7-Stomach-fact-sheet.pdf .
-
- Ministério da Saúde, Instituto Nacional de Câncer José Alencar Gomes da Silva. Estimativa 2020-Incidência de câncer no Brasil. 2019. [cited 11 January 2022]. Available from: https://www.inca.gov.br/sites/ufu.sti.inca.local/files//media/document//... .
-
- Yousefi B, Mohammadlou M, Abdollahi M, Salek Farrokhi A, Karbalaei M, Keikha M, Kokhaei P, Valizadeh S, Rezaiemanesh A, Arabkari V, Eslami M. Epigenetic changes in gastric cancer induction by Helicobacter pylori. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234:21770–21784. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

