Real-World data on efficacy of L-glutamine in preventing sickle cell disease-related complications in pediatric and adult patients
- PMID: 35979207
- PMCID: PMC9376442
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.931925
Real-World data on efficacy of L-glutamine in preventing sickle cell disease-related complications in pediatric and adult patients
Abstract
Background: L-glutamine has been shown to play an important role in the regulation of oxidative stress which is one of the key contributors to the pathophysiology of sickle cell disease (SCD). In a Phase 3 clinical trial, L-glutamine demonstrated a significant reduction in SCD-related complications including vaso-occlusive crises (VOCs), hospitalizations, and acute chest syndrome (ACS) compared to placebo in patients with SCD.
Objective: The primary objective was to confirm the efficacy of L-glutamine (Endari®) therapy in pediatric and adult patients with SCD at follow-up time points of 24, 48 and 72 weeks.
Methods: In the observational study, nineteen patients with SCD were treated orally with L-glutamine twice daily for 72 weeks. Clinical and laboratory parameters were measured at baseline and follow-up time points. Patients with severe VOC and ACS were hospitalized. Blood transfusion was given in case of ACS and uncontrolled pain associated with VOC despite administration of the highest dose of intravenous (IV) narcotic.
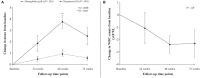
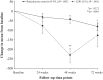
Results: Compared to baseline, patients had significantly fewer pain crises (median change from 3.0 to 0.0; P < 0.00001), hospitalizations (median change from 3.0 to 0.0; P < 0.00001), days of hospitalization (median change from 15.0 to 0.0; P < 0.00001), and blood transfusions (median change from 3.0 to 0.0; P < 0.00001) at 24, 48, and 72 weeks following L-glutamine therapy. Moreover, there was a drastic decrease in the number of ACS events during this time. A significant increase was observed in mean hemoglobin levels and hematocrit proportions from baseline to 72 weeks (P < 0.001). Conversely, compared to baseline, mean reticulocyte counts and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels were considerably lower at follow-up time points (P = 0.003 and P < 0.001, respectively). No patient reported treatment-related adverse events.
Conclusion: Although the sample size was small, our data clearly demonstrated that L-glutamine therapy was safe and significantly improved clinical outcomes and hemolysis parameters in patients with SCD.
Keywords: L-glutamine; clinical outcomes; hemolysis parameters; sickle cell disease; vaso-occlusive crisis.
Copyright © 2022 Elenga, Loko, Etienne-Julan, Al-Okka, Adel and Yassin.
Conflict of interest statement
NE and MY had received fees for consultancy from Emmaus Medical, Inc. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
"Long-term efficacy and safety of L-glutamine in preventing sickle cell disease-related acute complications and hemolysis in pediatric and adult patients-Real-world, observational study".Eur J Haematol. 2023 Jun;110(6):772-773. doi: 10.1111/ejh.13939. Epub 2023 Feb 20. Eur J Haematol. 2023. PMID: 36732400 No abstract available.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

