Preliminary evidence in treatment of eosinophilic gastroenteritis in children: A case series
- PMID: 35979287
- PMCID: PMC9294883
- DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i19.6417
Preliminary evidence in treatment of eosinophilic gastroenteritis in children: A case series
Abstract
Background: Eosinophilic gastroenteritis is a rare inflammatory disorder in children. However, there is still no standard guideline in the treatment of pediatric eosinophilic gastroenteritis.
Aim: To report our experience with the diagnosis and treatment of children with eosinophilic gastroenteritis.
Methods: From January 2017 to December 2019, a total of 22 children were diagnosed with eosinophilic gastroenteritis.
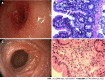
Results: Endoscopic examination showed eosinophil infiltration in the duodenum [mean number of eosinophils/high-power field (HPF) = 53.1 ± 81.5], stomach (mean number of eosinophils/HPF = 36.8 ± 50.5), and terminal ileum (mean number of eosinophils/HPF = 49.0 ± 24.0). All 18 children with low eosinophil infiltration (< 14%) responded well to the initial drug treatment without relapse, while two of four children with high eosinophil infiltration (> 14%) relapsed after initial methylprednisolone/montelukast treatment. In addition, children with high eosinophil infiltration (> 14%) showed symptomatic relief and histological remission without further relapse after receiving budesonide/methylprednisolone as initial or relapse treatment.
Conclusion: Methylprednisolone/montelukast is still the best treatment for children with low eosinophil infiltration (< 14%). Budesonide can be considered as the initial or relapse treatment for children with high eosinophil infiltration (> 14%).
Keywords: Absolute eosinophil count; Budesonide; Children; Eosinophil gastroenteritis; Methylprednisolone; Montelukast.
©The Author(s) 2022. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Eosinophilic gastroenteritis with persistent abdominal pain: a case report.J Rural Med. 2020 Jan;15(1):44-46. doi: 10.2185/jrm.2019-009. Epub 2020 Jan 23. J Rural Med. 2020. PMID: 32015781 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis of eosinophilic gastroenteritis is easily missed.World J Gastroenterol. 2017 May 21;23(19):3556-3564. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i19.3556. World J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28596692 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of 2 delivery vehicles for viscous budesonide to treat eosinophilic esophagitis in children.J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2014 Sep;59(3):317-20. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000000436. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2014. PMID: 24821535
-
Eosinophilic gastroenteritis.Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2002 Oct;4(5):366-72. doi: 10.1007/s11894-002-0006-2. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2002. PMID: 12228038 Review.
-
Eosinophilic gastroenteritis: A state-of-the-art review.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017 Jan;32(1):64-72. doi: 10.1111/jgh.13463. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017. PMID: 27253425 Review.
Cited by
-
Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders: a narrative review on clinical perspectives and research gaps in the Asian context.Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Aug 23;9:69. doi: 10.21037/tgh-24-34. eCollection 2024. Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 39503038 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Is Eosinophilic Colitis a Forerunner of Inflammatory Bowel Disease?Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2025 Aug 11;27(1):60. doi: 10.1007/s11894-025-01009-y. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40785002 Review.
References
-
- Licari A, Votto M, D'Auria E, Castagnoli R, Caimmi SME, Marseglia GL. Eosinophilic Gastrointestinal Diseases in Children: A Practical Review. Curr Pediatr Rev. 2020;16:106–114. - PubMed
-
- Grandinetti T, Biedermann L, Bussmann C, Straumann A, Hruz P. Eosinophilic Gastroenteritis: Clinical Manifestation, Natural Course, and Evaluation of Treatment with Corticosteroids and Vedolizumab. Dig Dis Sci. 2019;64:2231–2241. - PubMed
-
- Chen PH, Anderson L, Zhang K, Weiss GA. Eosinophilic Gastritis/Gastroenteritis. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2021;23:13. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

