Multimodal imaging study of lipemia retinalis with diabetic retinopathy: A case report
- PMID: 35979318
- PMCID: PMC9294873
- DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i19.6736
Multimodal imaging study of lipemia retinalis with diabetic retinopathy: A case report
Abstract
Background: Lipemia retinalis (LR) is a rare disease related to hypertriglyceridemia. However, the symptoms of hypertriglyceridemia are insidious and difficult to detect without blood tests. The fundus is the only site where blood vessels can be observed directly. Understanding the specific performance of LR in multimodal imaging fundus examinations can help diagnose more patients with abnormal hyperlipidemia.
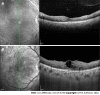
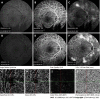
Case summary: A 29-year-old woman with type 2 diabetes presented to our clinic complaining of a six-day loss of visual acuity in the left eye. The fundus color images showed typical LR: Arteries and veins were the same pink-white color. Infrared images showed hyperinfrared reflections of the arteries and veins. Optical coherence tomography (OCT) showed numerous high point-like reflections in the retinal section, corresponding to different calibers of blood vessel sections. Medium reflections were seen in the big vessels of the choroid. Fundus fluorescein angiography (FFA) and optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA) showed no significant changes. Laboratory examination found a total cholesterol level of 13.98 mmol/L, triglyceride 20.55 mmol/L, which confirmed the diagnosis of LR. After treatment to lower blood lipids and control blood glucose, the fundus imaging showed that the blood lipids in the patient had returned to normal.
Conclusion: LR shows specific changes in fundus color photography, infrared photography, and OCT. FFA and OCTA were not sensitive to LR changes.
Keywords: Case report; Fundus color photography; Fundus fluorescein angiography; Infrared photography; Lipemia retinalis; Optical coherence tomography.
©The Author(s) 2022. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Case Report: Swept-source Optical Coherence Tomography and Angiography Findings in Lipemia Retinalis.Optom Vis Sci. 2022 Jan 1;99(1):76-81. doi: 10.1097/OPX.0000000000001830. Optom Vis Sci. 2022. PMID: 34882611
-
MULTICOLOR SCANNING LASER IMAGING IN LIPEMIA RETINALIS.Retin Cases Brief Rep. 2017 Winter;11 Suppl 1:S132-S135. doi: 10.1097/ICB.0000000000000469. Retin Cases Brief Rep. 2017. PMID: 27828900
-
Spectral-Domain Optical Coherence Tomography Findings in Lipemia Retinalis.Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging Retina. 2016 Jun 1;47(6):589-92. doi: 10.3928/23258160-20160601-13. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging Retina. 2016. PMID: 27327291
-
Retinal imaging in infants.Surv Ophthalmol. 2021 Nov-Dec;66(6):933-950. doi: 10.1016/j.survophthal.2021.01.011. Epub 2021 Jan 29. Surv Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 33524458 Review.
-
[A new approach for studying the retinal and choroidal circulation].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2004 Dec;108(12):836-61; discussion 862. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2004. PMID: 15656089 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
The Weight on Sight: Exploring the Links Between Obesity and Ocular Diseases.Cureus. 2024 Oct 30;16(10):e72742. doi: 10.7759/cureus.72742. eCollection 2024 Oct. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39483584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multimodal Retinal Imaging of Intravascular Lipid in Severe/Extreme Hypertriglyceridemia.Case Rep Ophthalmol Med. 2023 Sep 27;2023:6698239. doi: 10.1155/2023/6698239. eCollection 2023. Case Rep Ophthalmol Med. 2023. PMID: 37800092 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Leaf DA. Chylomicronemia and the chylomicronemia syndrome: a practical approach to management. Am J Med. 2008;121:10–12. - PubMed
-
- Gayathri K, Ramalingam PK, Santhakumar R, Manjunath BV, Karuppuswamy N, Vetriveran B, Selvamani S, Vishnuram P, Muruganathan A, Natarajan K. Lipemia Retinalis due to Secondary Hyperlipidemia in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. J Assoc Physicians India. 2016;64:83–84. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

