Field evaluation of COVID-19 rapid antigen test: Are rapid antigen tests less reliable among the elderly?
- PMID: 35979325
- PMCID: PMC9294881
- DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i19.6456
Field evaluation of COVID-19 rapid antigen test: Are rapid antigen tests less reliable among the elderly?
Abstract
Background: The global outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) leads to the development of accessible and cost-effective rapid antigen-detection tests (RATs), as quick and accurate diagnosis is crucial to curb the pandemic.
Aim: To evaluate the Humasis COVID-19 Ag Test (Humasis Co., Ltd., Gyeonggi-do, Republic of Korea) in the diagnosis of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2).
Methods: This retrospective study was carried out at the Croatian Institute of Public Health and included patients with clinical symptoms of COVID-19 lasting no longer than 5 d prior to testing, whose nasopharyngeal swabs were primarily tested with RAT. Negative RAT samples underwent confirmatory real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Diagnostic efficacy was determined compared to RT-PCR. The patients were divided into three age groups (< 18, 19-65, > 65 years). Statistical analysis was performed with the significance level set at P < 0.05.
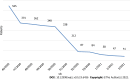
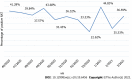
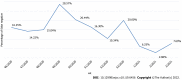
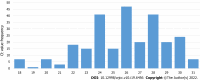
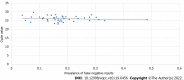
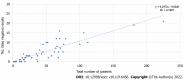
Results: In total, 2490 symptomatic patients were tested; 953 samples were positive on RAT, and 1537 were negative. All negative RAT samples were subjected to RT-PCR; 266 samples were positive and marked as false-negative results on RAT. The calculated negative predictive value as a measure of RAT efficacy was 82.69%. The χ 2 test and Kruskal-Wallis test showed a significant difference in the proportion of false negatives (P < 0.001) and RT-PCR cycle (Ct) values for false-negative RATs (P = 0.012) among the age groups. The young age group was significantly less likely to be false negative, whereas the false negatives from the elderly group experienced significantly lower Ct values than the other two age groups.
Conclusion: Evaluated RAT demonstrated satisfactory performance with more reliable results in younger patients. Humasis COVID-19 Ag RAT is potentially a valuable tool in areas where access to molecular methods is limited; however, RT-PCR remains a gold standard for SARS-CoV-2 detection.
Keywords: Coronavirus disease 2019; Croatia; Rapid antigen test; Real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction; Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2.
©The Author(s) 2022. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Evaluation of the Rapid Antigen Detection Kit with the Polymerase Chain Reaction for Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in Respiratory Samples].Mikrobiyol Bul. 2022 Apr;56(2):263-273. doi: 10.5578/mb.20229806. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2022. PMID: 35477229 Turkish.
-
Evaluation of Four Rapid Antigen Tests for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Infection with Nasopharyngeal Swabs.Biomedicines. 2023 Feb 24;11(3):701. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11030701. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36979680 Free PMC article.
-
An Agreement of Antigen Tests on Oral Pharyngeal Swabs or Less Invasive Testing With Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction for Detecting SARS-CoV-2 in Adults: Protocol for a Prospective Nationwide Observational Study.JMIR Res Protoc. 2022 May 4;11(5):e35706. doi: 10.2196/35706. JMIR Res Protoc. 2022. PMID: 35394449 Free PMC article.
-
[SARS-CoV-2 and Microbiological Diagnostic Dynamics in COVID-19 Pandemic].Mikrobiyol Bul. 2020 Jul;54(3):497-509. doi: 10.5578/mb.69839. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2020. PMID: 32755524 Review. Turkish.
-
Strategies to Overcome Erroneous Outcomes in Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) Testing: Insights From the COVID-19 Pandemic.Cureus. 2024 Nov 3;16(11):e72954. doi: 10.7759/cureus.72954. eCollection 2024 Nov. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39498425 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of COVID-19 rapid antigen test against polymerase chain reaction test in immunocompromised patients.PLoS One. 2024 Aug 2;19(8):e0306396. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0306396. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39093858 Free PMC article.
-
Ten rapid antigen tests for SARS-CoV-2 widely differ in their ability to detect Omicron-BA.4 and -BA.5.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2023 Oct;212(5):323-337. doi: 10.1007/s00430-023-00775-8. Epub 2023 Aug 10. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37561225 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid Antigen Tests during the COVID-19 Era in Korea and Their Implementation as a Detection Tool for Other Infectious Diseases.Bioengineering (Basel). 2023 Mar 3;10(3):322. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering10030322. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36978713 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of gender on the reliability of COVID-19 rapid antigen test among elderly.World J Clin Cases. 2022 Oct 16;10(29):10820-10822. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i29.10820. World J Clin Cases. 2022. PMID: 36312479 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Situation Report–51. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). [cited 20 March 2022]. Available from: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/2... . - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Laboratory testing for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in suspected human cases: interim guidance, March 2nd, 2020. [cited 20 March 2022]. Available from: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/331329 .
-
- World Health Organization. Antigen-detection in the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection using rapid immunoassays: interim guidance, September 11th, 2020. [cited 20 March 2022]. Available from: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/334253 .
-
- Vilibic-Cavlek T, Stevanovic V, Brlek-Gorski D, Ferencak I, Ferenc T, Ujevic-Bosnjak M, Tabain I, Janev-Holcer N, Perkovic I, Anticevic M, Bekavac B, Kaic B, Mrzljak A, Ganjto M, Zmak L, Mauric Maljkovic M, Jelicic P, Bucic L, Barbic L. Emerging Trends in the Epidemiology of COVID-19: The Croatian 'One Health' Perspective. Viruses . 2021;13 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alemany A, Baró B, Ouchi D, Rodó P, Ubals M, Corbacho-Monné M, Vergara-Alert J, Rodon J, Segalés J, Esteban C, Fernández G, Ruiz L, Bassat Q, Clotet B, Ara J, Vall-Mayans M, G-Beiras C, Blanco I, Mitjà O. Analytical and clinical performance of the panbio COVID-19 antigen-detecting rapid diagnostic test. J Infect . 2021;82:186–230. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

