YAP1 alleviates sepsis-induced acute lung injury via inhibiting ferritinophagy-mediated ferroptosis
- PMID: 35979359
- PMCID: PMC9376389
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.884362
YAP1 alleviates sepsis-induced acute lung injury via inhibiting ferritinophagy-mediated ferroptosis
Abstract
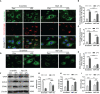
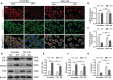
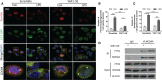
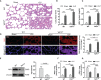
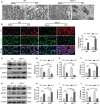
Ferroptosis is a phospholipid peroxidation-mediated and iron-dependent cell death form, involved in sepsis-induced organ injury and other lung diseases. Yes-associated protein 1 (YAP1), a key regulator of the Hippo signaling pathway, could target multiple ferroptosis regulators. Herein, this study aimed to explore the involvement of ferroptosis in the etiopathogenesis of sepsis-induced acute lung injury (ALI) and demonstrate that YAP1 could disrupt ferritinophagy and moderate sepsis-induced ALI. Cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) models were constructed in wild-type (WT) and pulmonary epithelium-conditional knockout (YAP1f/f) mice to induce ALI, while MLE-12 cells with or without YAP1 overexpression were stimulated by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in vitro. In-vivo modes showed that YAP1 knockout aggravated CLP-induced ALI and also accelerated pulmonary ferroptosis, as presented by the downregulated expression of GPX4, FTH1, and SLC7A11, along with the upregulated expression of SFXN1 and NCOA4. Transcriptome research identified these key genes and ferroptosis pathways involved in sepsis-induced ALI. In-vitro modes consistently verified that YAP1 deficiency boosted the ferrous iron accumulation and mitochondrial dysfunction in response to LPS. Furthermore, the co-IP assay revealed that YAP1 overexpression could prevent the degradation of ferritin to a mass of Fe2+ (ferritinophagy) via disrupting the NCOA4-FTH1 interaction, which blocked the transport of cytoplasmic Fe2+ into the mitochondria via the mitochondrial membrane protein (SFXN1), further reducing the generation of mitochondrial ROS. Therefore, these findings revealed that YAP1 could inhibit ferroptosis in a ferritinophagy-mediated manner, thus alleviating sepsis-induced ALI, which may provide a new approach to the therapeutic orientation for sepsis-induced ALI.
Keywords: NCOA4; YAP1; ferritinophagy; ferroptosis; sepsis-induced acute lung injury.
Copyright © 2022 Zhang, Zheng, Wang, Wang, Sang, Song and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Torio CM, Moore BJ. National inpatient hospital costs: The most expensive conditions by payer, 2013 Stat Brief. In: Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP) Statistical Briefs (2006) 204 Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US):Rockville (MD). - PubMed
-
- Hall MJ, Levant S, DeFrances CJ. Trends in inpatient hospital deaths: National hospital discharge survey, 2000-2010 NCHS Data Brief. US Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2013) 118):1–8. National Center for Health Statistics. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

