Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt with radioactive seed strand for main portal vein tumor thrombosis with cirrhotic portal hypertension
- PMID: 35979417
- PMCID: PMC9258232
- DOI: 10.4240/wjgs.v14.i6.567
Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt with radioactive seed strand for main portal vein tumor thrombosis with cirrhotic portal hypertension
Abstract
Background: Patients with hepatocellular carcinoma complicated with main portal vein tumor thrombosis (mPVTT) and cirrhotic portal hypertension (CPH) have an extremely poor prognosis, and there is a lack of a clinically effective treatment paradigm.
Aim: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) combined with radioactive seed strand for the treatment of mPVTT patients with CPH.
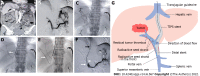
Methods: The clinical data of 83 consecutive patients who underwent TIPS combined with 125I seed strand placement for mPVTT and CPH from January 2015 to December 2018 were retrospectively reviewed. Procedure-related data (success rate, relief of portal vein pressure and CPH symptoms, and adverse events), PVTT response, and patient survival were assessed through a 2-year follow-up.
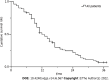
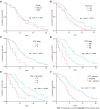
Results: The success rate was 100.0% without perioperative death or procedure-related severe adverse events. The mean portal vein pressure was significantly decreased after the procedure (22.25 ± 7.33 mmHg vs 35.12 ± 7.94 mmHg, t = 20.61, P < 0.001). The symptoms of CPH were all effectively relieved within 1 mo. The objective response rate of PVTT was 67.5%. During a mean follow-up of 14.5 ± 9.4 mo (range 1-37 mo), the cumulative survival rates at 6, 12 and 24 mo were 83.1%, 49.7%, and 21.8%, respectively. The median survival time was 12.0 ± 1.3 mo (95% confidence interval: 9.5-14.5). In multivariate Cox regression analysis, body mass index, Child-Pugh grade, cTNM stage, and PVTT response were independent prognostic factors (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: TIPS combined with radioactive seed strand might be effective and safe in treating mPVTT patients with CPH.
Keywords: Cirrhosis; Cirrhotic portal hypertension; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Portal vein tumor thrombosis; Radioactive seed strand; Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt.
©The Author(s) 2022. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures

References
-
- Zhang ZM, Lai EC, Zhang C, Yu HW, Liu Z, Wan BJ, Liu LM, Tian ZH, Deng H, Sun QH, Chen XP. The strategies for treating primary hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus. Int J Surg. 2015;20:8–16. - PubMed
-
- Shi J, Lai EC, Li N, Guo WX, Xue J, Lau WY, Wu MC, Cheng SQ. Surgical treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010;17:2073–2080. - PubMed
-
- Wang K, Guo WX, Chen MS, Mao YL, Sun BC, Shi J, Zhang YJ, Meng Y, Yang YF, Cong WM, Wu MC, Lau WY, Cheng SQ. Multimodality Treatment for Hepatocellular Carcinoma With Portal Vein Tumor Thrombus: A Large-Scale, Multicenter, Propensity Mathching Score Analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 2016;95:e3015. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kaneko S, Tsuchiya K, Yasui Y, Inada K, Kirino S, Yamashita K, Osawa L, Hayakawa Y, Sekiguchi S, Higuchi M, Takaura K, Maeyashiki C, Tamaki N, Takeguchi T, Takeguchi Y, Nagano T, Nakanishi H, Itakura J, Takahashi Y, Himeno Y, Hoshi A, Kurosaki M, Izumi N. Strategy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma based on liver function and portal vein tumor thrombosis. Hepatol Res. 2020;50:1375–1385. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

