Prognostic significance of the preoperative hemoglobin to albumin ratio for the short-term survival of gastric cancer patients
- PMID: 35979426
- PMCID: PMC9258240
- DOI: 10.4240/wjgs.v14.i6.580
Prognostic significance of the preoperative hemoglobin to albumin ratio for the short-term survival of gastric cancer patients
Abstract
Background: Hemoglobin and albumin are associated with the prognosis of gastric cancer (GC) patients. However, the prognostic value of the hemoglobin to albumin ratio (HAR) for the short-term survival of GC patients with D2 radical resection has not been studied.
Aim: To investigate the significance of the HAR in evaluating the short-term survival of GC patients after D2 radical resection and to construct a nomogram to predict the prognosis in GC patients after surgery, thus providing a reference for the development of postoperative individualized treatment and follow-up plans.
Methods: Cox regression and Kaplan-Meier analysis was used for prognostic analysis. Logistic regression was used to analyze the relationships between HAR and the clinicopathological characteristics of the GC patients. A prognostic nomogram model for the short-term survival of GC patients was constructed by R software.
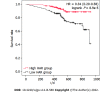
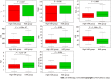
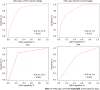
Results: HAR was an independent risk factor for the short-term survival of GC patients. GC patients with a low HAR had a poor prognosis (P < 0.001). Low HAR was markedly related to high stage [odds ratio (OR) = 0.45 for II vs I; OR = 0.48 for III vs I], T classification (OR = 0.52 for T4 vs T1) and large tumor size (OR = 0.51 for ≥ 4 cm vs < 4 cm) (all P < 0.05). The nomogram model was based on HAR, age, CA19-9, CA125 and stage, and the C-index was 0.820.
Conclusion: Preoperative low HAR was associated with short-term survival in GC patients. The prognostic nomogram model can accurately predict the short-term survival of GC patients with D2 radical resection.
Keywords: Gastric cancer; Hemoglobin to albumin ratio; Nomogram; Prognosis; Short-term survival.
©The Author(s) 2022. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Van Cutsem E, Sagaert X, Topal B, Haustermans K, Prenen H. Gastric cancer. Lancet. 2016;388:2654–2664. - PubMed
-
- Songun I, Putter H, Kranenbarg EM, Sasako M, van de Velde CJ. Surgical treatment of gastric cancer: 15-year follow-up results of the randomised nationwide Dutch D1D2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11:439–449. - PubMed
-
- Ajani JA, D'Amico TA, Almhanna K, Bentrem DJ, Chao J, Das P, Denlinger CS, Fanta P, Farjah F, Fuchs CS, Gerdes H, Gibson M, Glasgow RE, Hayman JA, Hochwald S, Hofstetter WL, Ilson DH, Jaroszewski D, Johung KL, Keswani RN, Kleinberg LR, Korn WM, Leong S, Linn C, Lockhart AC, Ly QP, Mulcahy MF, Orringer MB, Perry KA, Poultsides GA, Scott WJ, Strong VE, Washington MK, Weksler B, Willett CG, Wright CD, Zelman D, McMillian N, Sundar H. Gastric Cancer, Version 3.2016, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2016;14:1286–1312. - PubMed
-
- Shah MA, Ajani JA. Gastric cancer--an enigmatic and heterogeneous disease. JAMA. 2010;303:1753–1754. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

