Association of vision and hearing status with depressive symptoms among middle-aged and older Chinese adults
- PMID: 35979465
- PMCID: PMC9376298
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.857307
Association of vision and hearing status with depressive symptoms among middle-aged and older Chinese adults
Abstract
Objective: Long-term untreated vision and hearing impairments can negatively impact physical and mental wellbeing. We investigated the association of vision and hearing status with depressive symptoms among middle-aged and older Chinese adults.
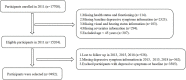
Methods: This was a prospective cohort study of 9,492 participants from the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study (CHARLS) carried out in 2011, 2013, 2015, and 2018. This study used self-reported vision and hearing status to determine the degree of impairment. Depressive symptoms were examined using the 10-item Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale (CESD-10), with a total score of ≥ 12 indicating depressive symptoms. A Cox proportional hazards model adjusted for age, sex, residence, marital status, educational level, smoking history, alcohol consumption, hypertension, diabetes, heart disease, digestive disease, arthritis, wearing glasses, and hearing aids was used to estimate the association of vision and hearing status with depressive symptoms among middle-aged and older Chinese adults.
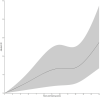
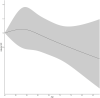
Results: Of the 9,492 participants [mean (SD) age at CHARLS baseline, 58.12 (9.00) years], 3,238 (34.11%) participants reported incident depressive symptoms during the 7-year follow-up period. Participants who self-reported only vision impairment [hazard ratios (HR): 1.14, 95% confidence intervals (CI): 1.05-1.24], only hearing impairment (HR: 1.24, 95% CI: 1.06-1.46), and both vision and hearing impairments (HR: 1.25, 95% CI: 1.08-1.45) were independently associated with a greater increase in the hazard risk of incident depressive symptoms compared to those without vision and hearing impairments. An increase in participants' vision and hearing scores was associated with a significant increase in the hazard risk of incident depressive symptoms (HR: 1.04, 95% CI: 1.03-1.06).
Conclusion: Vision and hearing status was associated with increased depressive symptoms among middle-aged and older Chinese adults during the 7-year follow-up period. Participants' use of glasses and hearing aids did not improve their depressive symptoms. Our findings may facilitate the development of effective treatments to prevent and treat vision and hearing impairments, thereby enhancing the physical and mental wellbeing of middle-aged and older adults.
Keywords: China; depressive symptoms; hearing impairment; older adults; vision impairment.
Copyright © 2022 Liu, Wang, Huang, Zhang and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of Depressive Symptoms With Incident Cardiovascular Diseases in Middle-Aged and Older Chinese Adults.JAMA Netw Open. 2019 Dec 2;2(12):e1916591. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.16591. JAMA Netw Open. 2019. PMID: 31800066 Free PMC article.
-
Association of changes in self-reported vision and hearing impairments with depressive symptoms in middle-aged and older adults: Evidence from a nationwide longitudinal study in China.Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2024 Jan;116:105131. doi: 10.1016/j.archger.2023.105131. Epub 2023 Jul 22. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2024. PMID: 37552924
-
The longitudinal effect of sensory loss on depression among Chinese older adults.J Affect Disord. 2021 Mar 15;283:216-222. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2021.01.081. Epub 2021 Feb 2. J Affect Disord. 2021. PMID: 33561802
-
Bidirectional associations of vision loss, hearing loss, and dual sensory loss with depressive symptoms among the middle-aged and older adults in China.J Affect Disord. 2022 Mar 15;301:225-232. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2022.01.066. Epub 2022 Jan 15. J Affect Disord. 2022. PMID: 35038482
-
Neural circuits and behavioral pathways linking hearing loss to affective dysregulation in older adults.Nat Aging. 2021 May;1(5):422-429. doi: 10.1038/s43587-021-00065-z. Epub 2021 May 14. Nat Aging. 2021. PMID: 37118018 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of intergenerational exchange patterns and intergenerational relationship quality on depressive symptoms in the elderly: An empirical study on CHARLS data.Front Public Health. 2022 Oct 3;10:1009781. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1009781. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36262237 Free PMC article.
-
Association of hearing loss and risk of depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Neurol. 2024 Oct 21;15:1446262. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1446262. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39497727 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of hearing ability on depression among retired middle-aged and elderly individuals in China: the chain mediating role of self-rated health and life satisfaction.J Health Popul Nutr. 2025 Mar 8;44(1):70. doi: 10.1186/s41043-025-00791-9. J Health Popul Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40057778 Free PMC article.
-
The Mediating Role of Depression in the Association Between Hearing Impairment and Functional Disability Among Middle-Aged and Older Adults in China.Innov Aging. 2023 Aug 29;7(8):igad093. doi: 10.1093/geroni/igad093. eCollection 2023. Innov Aging. 2023. PMID: 37841577 Free PMC article.
-
Configurational effects of intergenerational support on older adults' depression: an empirical study from CHARLS data.BMC Public Health. 2025 Jan 30;25(1):392. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-21532-x. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 39885421 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bourne RRA, Flaxman SR, Braithwaite T, Cicinelli MV, Das A, Jonas JB, et al. . Magnitude, temporal trends, and projections of the global prevalence of blindness and distance and near vision impairment: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob Health. (2017) 5:e888–97. 10.1016/S2214-109X(17)30293-0 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

