The integrase of genomic island GI sul2 mediates the mobilization of GI sul2 and IS CR-related element CR2- sul2 unit through site-specific recombination
- PMID: 35979485
- PMCID: PMC9376610
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.905865
The integrase of genomic island GI sul2 mediates the mobilization of GI sul2 and IS CR-related element CR2- sul2 unit through site-specific recombination
Abstract
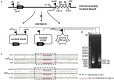
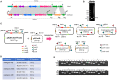
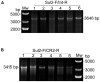
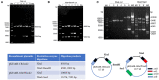
In the worldwide health threat posed by antibiotic-resistant bacterial pathogens, mobile genetic elements (MGEs) play a critical role in favoring the dissemination of resistance genes. Among them, the genomic island GIsul2 and the ISCR-related element CR2-sul2 unit are believed to participate in this dissemination. However, the mobility of the two elements has not yet been demonstrated. Here, we found that the GIsul2 and CR2-sul2 units can excise from the host chromosomal attachment site (attB) in Shigella flexneri. Through establishing a two-plasmid mobilization system composed of a donor plasmid bearing the GIsul2 and a trap plasmid harboring the attB in recA-deficient Escherichia coli, we reveal that the integrase of GIsul2 can perform the excision and integration of GIsul2 and CR2-sul2 unit by site-specific recombination between att core sites. Furthermore, we demonstrate that the integrase and the att sites are required for mobility through knockout experiments. Our findings provide the first experimental characterization of the mobility of GIsul2 and CR2-sul2 units mediated by integrase. They also suggest a potential and unappreciated role of the GIsul2 integrase family in the dissemination of CR2-sul2 units carrying various resistance determinants in between.
Keywords: ISCR elements; genomic island (GI); integrase; mobilization; site-specific recombination.
Copyright © 2022 Zhang, Cui, Li, Guo, Leclercq, Du, Tang, Song, Wang, Zhao and Feng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
pIP40a, a type 1 IncC plasmid from 1969 carries the integrative element GIsul2 and a novel class II mercury resistance transposon.Plasmid. 2017 Jul;92:17-25. doi: 10.1016/j.plasmid.2017.05.004. Epub 2017 May 31. Plasmid. 2017. PMID: 28577759
-
GIsul2, a genomic island carrying the sul2 sulphonamide resistance gene and the small mobile element CR2 found in the Enterobacter cloacae subspecies cloacae type strain ATCC 13047 from 1890, Shigella flexneri ATCC 700930 from 1954 and Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 17978 from 1951.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2011 Sep;66(9):2175-6. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkr230. Epub 2011 Jun 8. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2011. PMID: 21653606 No abstract available.
-
p39R861-4, A Type 2 A/C2 Plasmid Carrying a Segment from the A/C1 Plasmid RA1.Microb Drug Resist. 2015 Dec;21(6):571-6. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2015.0133. Epub 2015 Jul 13. Microb Drug Resist. 2015. PMID: 26167918
-
The Yersinia high-pathogenicity island (HPI): evolutionary and functional aspects.Int J Med Microbiol. 2004 Sep;294(2-3):83-94. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2004.06.026. Int J Med Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15493818 Review.
-
[Novel transmission element of antibiotic resistance genes ISCR and its ecological risk].Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 2015 Oct;26(10):3215-25. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 2015. PMID: 26995934 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Systematic Discovery of a New Catalogue of Tyrosine-Type Integrases in Bacterial Genomic Islands.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023 Feb 28;89(2):e0173822. doi: 10.1128/aem.01738-22. Epub 2023 Jan 31. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36719242 Free PMC article.
-
Persistence of commensal multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli in the broiler production pyramid is best explained by strain recirculation from the rearing environment.Front Microbiol. 2024 Jul 5;15:1406854. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1406854. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39035436 Free PMC article.
-
The environmental adaptation of acidophilic archaea: promotion of horizontal gene transfer by genomic islands.BMC Genomics. 2025 Jul 28;26(1):696. doi: 10.1186/s12864-025-11875-5. BMC Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40722006 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

