Intracellular communication and immunothrombosis in sepsis
- PMID: 35979601
- PMCID: PMC9804233
- DOI: 10.1111/jth.15852
Intracellular communication and immunothrombosis in sepsis
Abstract
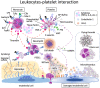
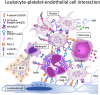
Inflammation and coagulation are the critical responses to infection that include leukocytes, platelets, and vascular endothelial cells responding in concert to eradicate the invading pathogen. In sepsis, a variety of cell surface receptors, including toll-like receptors, Fcγ-receptors, G-protein-coupled receptors, and adhesion receptors, detect the pathogens and elicit thromboinflammatory responses. Concurrently, the molecular patterns released from host damaged cells accelerate the immune responses through binding to the same pattern recognition receptors. Cytokines, chemokines, and extracellular vesicles are important mediators for amplifying the responses to distant cells as part of the systemic response to infections. At the same time, cells communicate with each other via direct contact, adhesion molecules, paracrine mediators, and tunneling nanotubes, which are important for regulating inflammation and thrombus formation. Despite increasing attention to immunothrombosis in sepsis, these close communication systems are less understood but play a critical role in host defense mechanisms. In this review, cellular activation and direct intercellular communication systems in sepsis with a focus on the coagulation response will be considered.
Keywords: adhesion molecule; endothelial cell; immunothrombosis; platelet; sepsis; thromboinflammation.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis.
Conflict of interest statement
TI has received a research grant from Japan Blood Products Organization and Asahi Kasei Pharmaceuticals. ML has received grants and has participated in advisory boards of NovoNordisk, Eli Lilly, Asahi Kasei Pharmaceuticals America, and Johnson & Johnson. JHL serves on the Steering Committees for Instrumentation Laboratories, Merck, and Octapharma.
Figures
References
-
- van der Poll T, Levi M. Crosstalk between inflammation and coagulation: the lessons of sepsis. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2012;10(5):632‐638. - PubMed
-
- Iba T, Levy JH. Inflammation and thrombosis: roles of neutrophils, platelets and endothelial cells and their interactions in thrombus formation during sepsis. J Thromb Haemost. 2018;16(2):231‐241. - PubMed
-
- Gando S, Levi M, Toh CH. Disseminated intravascular coagulation. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16037. - PubMed
-
- Iba T, Levy JH. Sepsis‐induced coagulopathy and disseminated intravascular coagulation. Anesthesiology. 2020;132(5):1238‐1245. - PubMed
-
- Martinod K, Deppermann C. Immunothrombosis and thromboinflammation in host defense and disease. Platelets. 2021;32(3):314‐324. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

