FAM135B sustains the reservoir of Tip60-ATM assembly to promote DNA damage response
- PMID: 35979619
- PMCID: PMC9386324
- DOI: 10.1002/ctm2.945
FAM135B sustains the reservoir of Tip60-ATM assembly to promote DNA damage response
Abstract
Background: Recently, the mechanism by which cells adapt to intrinsic and extrinsic stresses has received considerable attention. Tat-interactive protein 60-kDa/ataxia-telangiectasia-mutated (TIP60/ATM) axis-mediated DNA damage response (DDR) is vital for maintaining genomic integrity.
Methods: Protein levels were detected by western blot, protein colocalisation was examined by immunofluorescence (IF) and protein interactions were measured by co-immunoprecipitation, proximity ligation assay and GST pull-down assays. Flow cytometry, comet assay and IF assays were used to explore the biological functions of sequence similarity 135 family member B (FAM135B) in DDR. Xenograft tumour, FAM135B transgenic mouse models and immunohistochemistry were utilised to confirm in vitro observations.
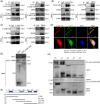
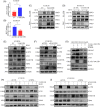
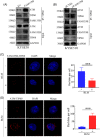
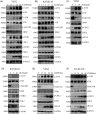
Results: We identified a novel DDR regulator FAM135B which could protect cancer cells from genotoxic stress in vitro and in vivo. The overexpression of FAM135B promoted the removal of γH2AX and 53BP1 foci, whereas the elimination of FAM135B attenuated these effects. Consistently, our findings revealed that FAM135B could promote homologous recombination and non-homologous end-joining repairs. Further study demonstrated that FAM135B physically bound to the chromodomain of TIP60 and improved its histone acetyltransferase activity. Moreover, FAM135B enhanced the interactions between TIP60 and ATM under resting conditions. Intriguingly, the protein levels of FAM135B dramatically decreased following DNA damage stress but gradually increased during the DNA repair period. Thus, we proposed a potential DDR mechanism where FAM135B sustains a reservoir of pre-existing TIP60-ATM assemblies under resting conditions. Once cancer cells suffer DNA damage, FAM135B is released from TIP60, and the functioning pre-assembled TIP60-ATM complex participates in DDR.
Conclusions: We characterised FAM135B as a novel DDR regulator and further elucidated the role of the TIP60-ATM axis in response to DNA damage, which suggests that targeting FAM135B in combination with radiation therapy or chemotherapy could be a potentially effective approach for cancer treatment.
© 2022 The Authors. Clinical and Translational Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Shanghai Institute of Clinical Bioinformatics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Functional Characterization of ATM Kinase Using Acetylation-Specific Antibodies.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1599:157-162. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6955-5_12. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28477118
-
An insight into understanding the coupling between homologous recombination mediated DNA repair and chromatin remodeling mechanisms in plant genome: an update.Cell Cycle. 2021 Sep;20(18):1760-1784. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2021.1966584. Epub 2021 Aug 26. Cell Cycle. 2021. PMID: 34437813 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A role for the Tip60 histone acetyltransferase in the acetylation and activation of ATM.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Sep 13;102(37):13182-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0504211102. Epub 2005 Sep 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 16141325 Free PMC article.
-
Thymidylate kinase is critical for DNA repair via ATM-dependent Tip60 complex formation.FASEB J. 2019 Feb;33(2):2017-2025. doi: 10.1096/fj.201800856R. Epub 2018 Sep 10. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 30199284
-
Tip60: updates.J Appl Genet. 2018 May;59(2):161-168. doi: 10.1007/s13353-018-0432-y. Epub 2018 Mar 16. J Appl Genet. 2018. PMID: 29549519 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluating the Cellular Roles of the Lysine Acetyltransferase Tip60 in Cancer: A Multi-Action Molecular Target for Precision Oncology.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jul 27;16(15):2677. doi: 10.3390/cancers16152677. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39123405 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The mechanism and clinical application of DNA damage repair inhibitors combined with immune checkpoint inhibitors in the treatment of urologic cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 May 25;11:1200466. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1200466. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37305685 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in the Histone Acetylation Modification in the Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.J Oncol. 2023 Feb 9;2023:4616682. doi: 10.1155/2023/4616682. eCollection 2023. J Oncol. 2023. PMID: 39282225 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aberrant FAM135B attenuates the efficacy of chemotherapy in colorectal cancer by modulating SRSF1-mediated alternative splicing.Oncogene. 2024 Nov;43(48):3532-3544. doi: 10.1038/s41388-024-03189-9. Epub 2024 Oct 13. Oncogene. 2024. PMID: 39397154
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
