Comparative analysis of galactomannan lateral flow assay, galactomannan enzyme immunoassay and BAL culture for diagnosis of COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis
- PMID: 35979737
- PMCID: PMC9538082
- DOI: 10.1111/myc.13518
Comparative analysis of galactomannan lateral flow assay, galactomannan enzyme immunoassay and BAL culture for diagnosis of COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis
Abstract
Background: Galactomannan Enzyme Immunoassay (GM-EIA) is proved to be a cornerstone in the diagnosis of COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis (CAPA), its use is limited in middle and low-income countries, where the application of simple and rapid test, including Galactomannan Lateral Flow Assay (GM-LFA), is highly appreciated. Despite such merits, limited studies directly compared GM-LFA with GM-EIA. Herein we compared the diagnostic features of GM-LFA, GM-EIA and bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) culture for CAPA diagnosis in Iran, a developing country.
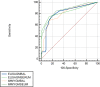
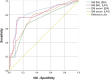
Materials/methods: Diagnostic performances of GM-LFA and GM-EIA in BAL (GM indexes ≥1) and serum (GM indexes >0.5), i.e. sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV) and negative predictive value (NPV) and areas under the curve (AUC), were evaluated using BAL (n = 105) and serum (n = 101) samples from mechanically ventilated COVID-19 patients in intensive care units. Patients were classified based on the presence of host factors, radiological findings and mycological evidences according to 2020 ECMM/ISHAM consensus criteria for CAPA diagnosis.
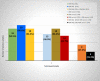
Results: The Aspergillus GM-LFA for serum and BAL samples showed a sensitivity of 56.3% and 60.6%, specificity of 94.2% and 88.9%, PPV of 81.8% and 71.4%, NPV of 82.3% and 83.1%, when compared with BAL culture, respectively. GM-EIA showed sensitivities of 46.9% and 54.5%, specificities of 100% and 91.7%, PPVs of 100% and 75%, NPVs of 80.2% and 81.5% for serum and BAL samples, respectively.
Conclusion: Our study found GM-LFA as a reliable simple and rapid diagnostic tool, which could circumvent the shortcomings of culture and GM-EIA and be pivotal in timely initiation of antifungal treatment.
Keywords: COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis; culture; galactomannan enzyme immunoassay; galactomannan lateral flow assay.
© 2022 Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
Martin Hoenigl received research funding from Astellas, Euroimmune, Pfizer, Gilead, Scynexis, MSD and NIH. All other authors declared no potential conflict of interest of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of the Equivalence of Aspergillus Antigen and PCR Results Between Non-Directed Bronchial Lavage and Bronchoalveolar Lavage-A Prospective Exploratory Pilot Study in Critically Ill Patients.Mycoses. 2025 Feb;68(2):e70029. doi: 10.1111/myc.70029. Mycoses. 2025. PMID: 39900777 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic Efficacy of Aspergillus Galactomannan Lateral Flow Assay in Patients with Hematological Malignancies: A Prospective Multicenter Study.Mycopathologia. 2023 Oct;188(5):643-653. doi: 10.1007/s11046-023-00749-7. Epub 2023 Jun 5. Mycopathologia. 2023. PMID: 37273172 Free PMC article.
-
Usefulness of Sōna Aspergillus Galactomannan LFA with digital readout as diagnostic and as screening tool of COVID-19 associated pulmonary aspergillosis in critically ill patients. Data from a multicenter prospective study performed in Argentina.Med Mycol. 2022 May 18;60(5):myac026. doi: 10.1093/mmy/myac026. Med Mycol. 2022. PMID: 35394043 Free PMC article.
-
Performance of the IMMY® sona Aspergillus lateral flow assay for the detection of galactomannan in tracheal aspirate samples from Brazilian patients with COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis: Cross-sectional and systematic review of literature.Mycoses. 2024 Aug;67(8):e13789. doi: 10.1111/myc.13789. Mycoses. 2024. PMID: 39179520
-
The Value of the Galactomannan Test in Diagnosing COVID-19-Associated Pulmonary Aspergillosis: A Review.Iran J Pathol. 2025 Spring;20(2):142-151. doi: 10.30699/ijp.2025.2044324.3369. Epub 2025 Mar 10. Iran J Pathol. 2025. PMID: 40487254 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnosis and Outcomes of Fungal Co-Infections in COVID-19 Infections: A Retrospective Study.Microorganisms. 2023 Sep 15;11(9):2326. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11092326. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37764170 Free PMC article.
-
Antifungal stewardship in critically ill patients.Intensive Care Med. 2023 Jun;49(6):681-684. doi: 10.1007/s00134-023-07034-7. Epub 2023 Mar 24. Intensive Care Med. 2023. PMID: 36961529 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Lateral flow assay (LFA) in the diagnosis of COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis (CAPA): a single-center experience.BMC Infect Dis. 2022 Nov 8;22(1):822. doi: 10.1186/s12879-022-07828-y. BMC Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 36348480 Free PMC article.
-
Implementation of Lateral Flow Assays for the Diagnosis of Invasive Aspergillosis in European Hospitals: A Survey from Belgium and a Literature Review of Test Performances in Different Patient Populations.Mycopathologia. 2023 Oct;188(5):655-665. doi: 10.1007/s11046-023-00739-9. Epub 2023 May 20. Mycopathologia. 2023. PMID: 37209228
-
Microbiological Non-Culture-Based Methods for Diagnosing Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in ICU Patients.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Aug 21;13(16):2718. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13162718. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37627977 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cornely OA, Lass‐Flörl C, Lagrou K, Arsic‐Arsenijevic V, Hoenigl M. Improving outcome of fungal diseases–guiding experts and patients towards excellence. Mycoses. 2017;60(7):420‐425. - PubMed
-
- Koulenti D, Garnacho‐Montero J, Blot S. Approach to invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in critically ill patients. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2014;27(2):174‐183. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

