Focal sources of FGF-10 promote the buckling morphogenesis of the embryonic airway epithelium
- PMID: 35979841
- PMCID: PMC9536751
- DOI: 10.1242/bio.059436
Focal sources of FGF-10 promote the buckling morphogenesis of the embryonic airway epithelium
Abstract
During airway branching morphogenesis, focal regions of FGF-10 expression in the pulmonary mesenchyme are thought to provide a local guidance cue, which promotes chemotactically the directional outgrowth of the airway epithelium. Here, however, we show that an ectopic source of FGF-10 induces epithelial buckling morphogenesis and the formation of multiple new supernumerary buds. FGF-10-induced budding can be modulated by altered epithelial tension and luminal fluid pressure. Increased tension suppresses the formation of ectopic branches, while a collapse of the embryonic airway promotes more expansive buckling and additional FGF-10-induced supernumerary buds. Our results indicate that a focal source of FGF-10 can promote epithelial buckling and suggest that the overall branching pattern cannot be explained entirely by the templated expression of FGF-10. Both FGF-10-mediated cell behaviors and exogenous mechanical forces must be integrated to properly shape the bronchial tree.
Keywords: Biomechanics; Branching morphogenesis; Chick embryo; Lung development; Mechanobiology.
© 2022. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures
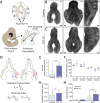
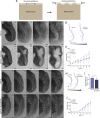
 for explants cultured with either PBS- or FGF-10 loaded beads, where L is the measured length of the ventral epithelium at each time-point,
for explants cultured with either PBS- or FGF-10 loaded beads, where L is the measured length of the ventral epithelium at each time-point,  is the length of the straight line connecting the endpoints of L, and L0 is the length of the ventral epithelium at t=0 h, which is used as a reference length. A Student's unpaired t-test (E,G) or a one-way ANOVA (H), followed by a Tukey post-hoc test, were used to make statistical comparisons. (PBS: n=29, FGF-10: n=37; *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001; error bars represent s.d.).
is the length of the straight line connecting the endpoints of L, and L0 is the length of the ventral epithelium at t=0 h, which is used as a reference length. A Student's unpaired t-test (E,G) or a one-way ANOVA (H), followed by a Tukey post-hoc test, were used to make statistical comparisons. (PBS: n=29, FGF-10: n=37; *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001; error bars represent s.d.).


Similar articles
-
Fluid secretion and luminal pressure control lateral branching morphogenesis in the embryonic avian lung.Dev Biol. 2025 Apr;520:251-263. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2025.01.016. Epub 2025 Jan 25. Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 39870322
-
Region- and stage-specific effects of FGFs and BMPs in chick mandibular morphogenesis.Dev Dyn. 2002 Mar;223(3):333-52. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.10056. Dev Dyn. 2002. PMID: 11891984
-
FGF-10 is a chemotactic factor for distal epithelial buds during lung development.Dev Biol. 1998 Sep 15;201(2):125-34. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1998.8994. Dev Biol. 1998. PMID: 9740653
-
Sonic hedgehog regulates branching morphogenesis in the mammalian lung.Curr Biol. 1998 Sep 24;8(19):1083-6. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(98)70446-4. Curr Biol. 1998. PMID: 9768363 Review.
-
Bud, branch, breathe! Building a mammalian lung over space and time.Dev Biol. 2025 Jun;522:64-75. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2025.03.010. Epub 2025 Mar 17. Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40107482 Review.
Cited by
-
Stem cells, cell therapies, and bioengineering in lung biology and diseases 2023.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2024 Sep 1;327(3):L327-L340. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00052.2024. Epub 2024 May 21. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38772903 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vitro biomimetic models for respiratory diseases: progress in lung organoids and lung-on-a-chip.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025 Jul 30;16(1):415. doi: 10.1186/s13287-025-04500-5. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40739651 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

