HER2 drives lung fibrosis by activating a metastatic cancer signature in invasive lung fibroblasts
- PMID: 35980387
- PMCID: PMC9391950
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20220126
HER2 drives lung fibrosis by activating a metastatic cancer signature in invasive lung fibroblasts
Abstract
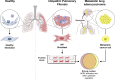
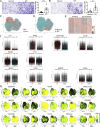
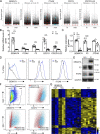
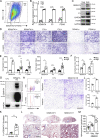
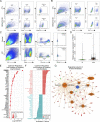
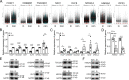
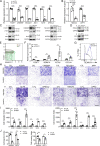
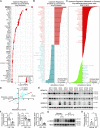
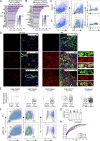
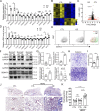
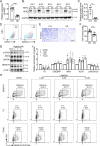
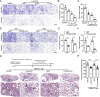
Progressive tissue fibrosis, including idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), is characterized by excessive recruitment of fibroblasts to sites of tissue injury and unremitting extracellular matrix deposition associated with severe morbidity and mortality. However, the molecular mechanisms that control progressive IPF have yet to be fully determined. Previous studies suggested that invasive fibroblasts drive disease progression in IPF. Here, we report profiling of invasive and noninvasive fibroblasts from IPF patients and healthy donors. Pathway analysis revealed that the activated signatures of the invasive fibroblasts, the top of which was ERBB2 (HER2), showed great similarities to those of metastatic lung adenocarcinoma cancer cells. Activation of HER2 in normal lung fibroblasts led to a more invasive genetic program and worsened fibroblast invasion and lung fibrosis, while antagonizing HER2 signaling blunted fibroblast invasion and ameliorated lung fibrosis. These findings suggest that HER2 signaling may be a key driver of fibroblast invasion and serve as an attractive target for therapeutic intervention in IPF.
© 2022 Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: B.R. Stripp reported grants from Bristol Myers Squibb outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
Figures


Similar articles
-
PD-L1 on invasive fibroblasts drives fibrosis in a humanized model of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.JCI Insight. 2019 Mar 21;4(6):e125326. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.125326. eCollection 2019 Mar 21. JCI Insight. 2019. PMID: 30763282 Free PMC article.
-
Adiponectin suppresses stiffness-dependent, profibrotic activation of lung fibroblasts.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2024 Oct 1;327(4):L487-L502. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00037.2024. Epub 2024 Aug 6. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39104319 Free PMC article.
-
Hsp90 regulation of fibroblast activation in pulmonary fibrosis.JCI Insight. 2017 Feb 23;2(4):e91454. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.91454. JCI Insight. 2017. PMID: 28239659 Free PMC article.
-
Lung Fibroblasts, Aging, and Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2016 Dec;13 Suppl 5:S417-S421. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201605-341AW. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2016. PMID: 28005427 Review.
-
Osteopontin: an essential regulatory protein in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.J Mol Histol. 2024 Feb;55(1):1-13. doi: 10.1007/s10735-023-10169-y. Epub 2023 Oct 25. J Mol Histol. 2024. PMID: 37878112 Review.
Cited by
-
Multiple Fibroblast Subtypes Contribute to Matrix Deposition in Pulmonary Fibrosis.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2023 Jul;69(1):45-56. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2022-0292OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36927333 Free PMC article.
-
Caveolin-1-Related Intervention for Fibrotic Lung Diseases.Cells. 2023 Feb 9;12(4):554. doi: 10.3390/cells12040554. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36831221 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MHIF-MSEA: a novel model of miRNA set enrichment analysis based on multi-source heterogeneous information fusion.Front Genet. 2024 Mar 22;15:1375148. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1375148. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 38586586 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor suppressors RBL1 and PTEN are epigenetically silenced in IPF mesenchymal progenitor cells by a CD44/Brg1/PRMT5 regulatory complex.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2024 Dec 1;327(6):L949-L963. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00182.2024. Epub 2024 Oct 15. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39406384
-
Pulmonary fibrosis: pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies.MedComm (2020). 2024 Sep 23;5(10):e744. doi: 10.1002/mco2.744. eCollection 2024 Oct. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 39314887 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adams, T.S., Schupp J.C., Poli S., Ayaub E.A., Neumark N., Ahangari F., Chu S.G., Raby B.A., DeIuliis G., Januszyk M., et al. . 2020. Single-cell RNA-seq reveals ectopic and aberrant lung-resident cell populations in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Sci. Adv. 6:eaba1983. 10.1126/sciadv.aba1983 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Artaud-Macari, E., Goven D., Brayer S., Hamimi A., Besnard V., Marchal-Somme J., Ali Z.E., Crestani B., Kerdine-Romer S., Boutten A., and Bonay M.. 2013. Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 nuclear translocation induces myofibroblastic dedifferentiation in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 18:66–79. 10.1089/ars.2011.4240 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Baughman, R.P., Lower E.E., Miller M.A., Bejarano P.A., and Heffelfinger S.C.. 1999. Overexpression of transforming growth factor-α and epidermal growth factor-receptor in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffuse Lung Dis. 16:57–61 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

