Validated allergen exposure chamber is plausible tool for the assessment of house dust mite-triggered allergic rhinitis
- PMID: 35980665
- PMCID: PMC10087469
- DOI: 10.1111/all.15485
Validated allergen exposure chamber is plausible tool for the assessment of house dust mite-triggered allergic rhinitis
Abstract
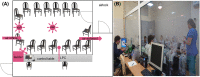
Background: Allergen exposure chamber (AEC) is a clinical facility that allows exposure to allergenic airborne particles in controlled environment. Although AECs offer stable levels of airborne allergens, the validation of symptoms and other endpoints induced by allergen challenge is key for their recommendation as a plausible tool for the assessment of patients, especially in clinical research. This study aimed to demonstrate the reproducibility of defined clinical endpoints after AEC house dust mite (HDM) challenge under optimal conditions in patients with allergic rhinitis (AR).
Method: HDM was distributed at different concentrations. The assessment was subjective by the patients: total nasal symptom score (TNSS), visual analog scale (VAS), and objective by the investigator: acoustic rhinometry, peak nasal inspiratory flow (PNIF), and nasal secretion weight. Safety was assessed clinically and by peak expiratory flow rate (PEFR) and forced expiratory volume in the first second (FEV1 ).
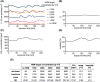
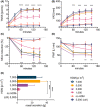
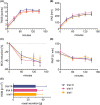
Results: Constant environment: temperature, humidity, and carbon dioxide (CO2 ) concentration were maintained during all challenges. The concentration of HDM on average remained stable within the targeted values: 1000, 3000, 5000, 7000 particles (p)/m3 . Most symptoms were observed at concentrations 3000 p/m3 or higher. The symptoms severity and other endpoints results were reproducible. 5000 p/m3 , and challenge duration of 120 min were found optimal. The procedure was safe with no lung function abnormalities due to challenge.
Conclusion: HDM challenge in ALL-MED AEC offers a safe and reliable method for inducing symptoms in AR patients for the use in controlled clinical studies including allergen immunotherapy.
Keywords: acoustic rhinometry; allergen challenge; allergen exposure chamber; allergic rhinitis; house dust mite.
© 2022 The Authors. Allergy published by European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
MJ reports personal fees from ALK‐Abello, Allergopharma, Stallergenes, Anergis, Allergy Therapeutics, Leti, HAL, GSK, Novartis, Teva, Takeda, and Chiesi. All other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Symptom Assessment of Patients with Allergic Rhinitis Using an Allergen Exposure Chamber.J Vis Exp. 2023 Mar 3;(193). doi: 10.3791/64801. J Vis Exp. 2023. PMID: 36939263
-
[Efficacy comparison and safety analysis of subcutaneous specific immunotherapy with standardized house dust mite allergen in patients with single and multiple allergic rhinitis].Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2022 Jun 6;56(6):774-783. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112150-20220120-00071. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35785859 Chinese.
-
Clinical validation of grass pollen exposure chamber in patients with allergic rhinitis triggered by timothy grass.Clin Exp Allergy. 2024 Jul;54(7):489-499. doi: 10.1111/cea.14482. Epub 2024 Apr 14. Clin Exp Allergy. 2024. PMID: 38616622
-
The effect of immunotherapy on cross-reactivity between house dust mite and other allergens in house dust mite -sensitized patients with allergic rhinitis.Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2021 Sep;17(9):969-975. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2021.1968834. Epub 2021 Aug 18. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34388949 Review.
-
House dust mite allergen immunotherapy for monosensitized versus polysensitized patients with allergic rhinitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2022 Dec 1;40(4):337-352. doi: 10.12932/AP-190822-1440. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36278778
Cited by
-
Immunological mechanisms of tolerance: Central, peripheral and the role of T and B cells.Asia Pac Allergy. 2023 Dec;13(4):175-186. doi: 10.5415/apallergy.0000000000000128. Epub 2023 Dec 8. Asia Pac Allergy. 2023. PMID: 38094089 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Modern Approach to Clinical Outcome Assessment in Allergy Management: Advantages of Allergen Exposure Chambers.J Clin Med. 2024 Nov 29;13(23):7268. doi: 10.3390/jcm13237268. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39685727 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Update on HDM Allergy: Principal Changes over the Years.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 13;26(12):5660. doi: 10.3390/ijms26125660. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40565123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of ZNF608 Polymorphisms With House Dust Mite-Induced Allergic Rhinitis.Clin Transl Allergy. 2025 Aug;15(8):e70081. doi: 10.1002/clt2.70081. Clin Transl Allergy. 2025. PMID: 40765419 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Evaluation of an Allergen Exposure Chamber and Nasal Allergen Challenge Versus In-Field Symptom Assessment in Patients With Allergic Rhinitis Triggered by Timothy Grass Pollen.Allergy. 2025 May;80(5):1286-1297. doi: 10.1111/all.16518. Epub 2025 Mar 9. Allergy. 2025. PMID: 40059339 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

