Asymmetric Organocatalytic Homologation: Access to Diverse Chiral Trifluoromethyl Organoboron Species
- PMID: 35980871
- PMCID: PMC9804810
- DOI: 10.1002/chem.202202059
Asymmetric Organocatalytic Homologation: Access to Diverse Chiral Trifluoromethyl Organoboron Species
Abstract
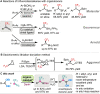
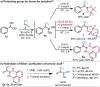
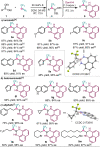
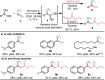
A broad range of aliphatic, aromatic, and heterocyclic boronic acids were successfully homologated using trifluorodiazoethane in the presence of BINOL derivatives to provide the corresponding chiral trifluoromethyl containing boronic acid derivatives in high yields and excellent enantioselectivity. The in situ conversion of the chiral transient boronic acids to the corresponding alcohols or β-CF3 carboxylates are also demonstrated.
Keywords: asymmetric homologation; enantioselective; organoboron; organocatalysis; organofluorine.
© 2022 The Authors. Chemistry - A European Journal published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Pavel M., Gross D. J., Benavent M., Perros P., Srirajaskanthan R., Warner R. R. P., Kulke M. H., Anthony L. B., Kunz P. L., Hörsch D., Weickert M. O., Lapuerta P., Jiang W., Kassler-Taub K., Wason S., Fleming R., Fleming D., Garcia-Carbonero R., Endocr.-Relat. Cancer 2018, 25, 309–22. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pinard E., Alanine A., Alberati D., Bender M., Borroni E., Bourdeaux P., Brom V., Burner S., Fischer H., Hainzl D., Halm R., Hauser N., Jolidon S., Lengyel J., Marty H.-P., Meyer T., Moreau J.-L., Mory R., Narquizian R., Nettekoven M., Norcross R. D., Puellmann B., Schmid P., Schmitt S., Stalder H., Wermuth R., Wettstein J. G., Zimmerli D., J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 4603–14. - PubMed
-
- Fernandes G. F. S., Denny W. A., Dos Santos J. L., Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 179, 791–804. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

