Interoceptive accuracy and bias in somatic symptom disorder, illness anxiety disorder, and functional syndromes: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 35980959
- PMCID: PMC9387777
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0271717
Interoceptive accuracy and bias in somatic symptom disorder, illness anxiety disorder, and functional syndromes: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Somatic symptom disorder, illness anxiety disorder, and functional syndromes are characterized by burdensome preoccupation with somatic symptoms. Etiological models propose either increased interoceptive accuracy through hypervigilance to the body, or decreased and biased interoception through top-down predictions about sensory events. This systematic review and meta-analysis summarizes findings of 68 studies examining interoceptive accuracy and 8 studies examining response biases in clinical or non-clinical groups. Analyses yielded a medium population effect size for decreased interoceptive accuracy in functional syndromes, but no observable effect in somatic symptom disorder and illness anxiety disorder. The overall effect size was highly heterogeneous. Regarding response bias, there was a small significant effect in somatic symptom disorder and illness anxiety disorder. Our findings strengthen the notion of top-down factors that result in biased rather than accurate perception of body signals in somatic symptom disorder and illness anxiety disorder.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
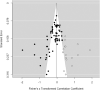
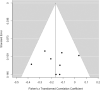
Figures

References
-
- Crane D, Morton L., Fawcett D., Moore A., Larson J., & Sandberg J. Somatoform Disorder: Treatment Utlization and Cost by Mental Health Professions. Contemporary Family Therapy. 2012;34:322–33.
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

