Influence of posterior tibial slope on sagittal knee alignment with comparing contralateral knees of anterior cruciate ligament injured patients to healthy knees
- PMID: 35982105
- PMCID: PMC9388669
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-18442-y
Influence of posterior tibial slope on sagittal knee alignment with comparing contralateral knees of anterior cruciate ligament injured patients to healthy knees
Abstract
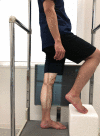
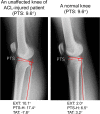
Posterior tibial slope (PTS) has been known to contribute to anterior-posterior knee stability and play an essential biomechanical role in knee kinematics. This study aimed to investigate the effect of PTS on single-leg standing sagittal knee alignment of the intact knee. This study included 100 patients with unilateral ACL injury knee (ACL injury group, 53 patients) or with the normal knee (control group, 47 patients). The single-leg standing sagittal alignment of the unaffected knees of the ACL injury group and normal knees of the control group were assessed radiographically with the following parameters: knee extension angle (EXT), PTS, PTS to the horizontal line (PTS-H), femoral shaft anterior tilt to the vertical axis (FAT), and tibial shaft anterior tilt to the vertical axis (TAT). PTS was negatively correlated with EXT and positively correlated with TAT. EXT was significantly larger in the ACL injury group, whereas TAT was smaller in the ACL injury group. Patients with larger PTS tend to stand with a higher knee flexion angle by tilting the tibia anteriorly, possibly reducing tibial shear force. Patients with ACL injury tend to stand with larger EXT, i.e., there is less preventive alignment to minimize the tibial shear force.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Variations in Knee Kinematics After ACL Injury and After Reconstruction Are Correlated With Bone Shape Differences.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017 Oct;475(10):2427-2435. doi: 10.1007/s11999-017-5368-8. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017. PMID: 28451863 Free PMC article.
-
Graft position in arthroscopic anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: anteromedial versus transtibial technique.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2016 Nov;136(11):1571-1580. doi: 10.1007/s00402-016-2532-7. Epub 2016 Aug 2. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2016. PMID: 27484876
-
High posterior tibial slope increases anterior cruciate ligament elongation in unicompartmental knee arthroplasty during early-flexion of lunge.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025 Apr 21;26(1):382. doi: 10.1186/s12891-025-08335-2. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025. PMID: 40259297 Free PMC article.
-
The Influence of Tibial and Femoral Bone Morphology on Knee Kinematics in the Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injured Knee.Clin Sports Med. 2018 Jan;37(1):127-136. doi: 10.1016/j.csm.2017.07.012. Epub 2017 Sep 6. Clin Sports Med. 2018. PMID: 29173552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of the tibial slope in sustaining and treating anterior cruciate ligament injuries.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013 Jan;21(1):134-45. doi: 10.1007/s00167-012-1941-6. Epub 2012 Mar 7. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013. PMID: 22395233 Review.
Cited by
-
Assessing joint line obliquity in valgus-producing high tibial osteotomy: A scoping review of the literature.J Orthop. 2025 Jan 15;67:94-100. doi: 10.1016/j.jor.2025.01.021. eCollection 2025 Sep. J Orthop. 2025. PMID: 39906180 Review.
-
Change of leg length after closed wedge high tibial osteotomy and associated factors.J Orthop Surg Res. 2025 Feb 14;20(1):163. doi: 10.1186/s13018-025-05582-w. J Orthop Surg Res. 2025. PMID: 39953526 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

