Biophysical differences in IgG1 Fc-based therapeutics relate to their cellular handling, interaction with FcRn and plasma half-life
- PMID: 35982144
- PMCID: PMC9388496
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-022-03787-x
Biophysical differences in IgG1 Fc-based therapeutics relate to their cellular handling, interaction with FcRn and plasma half-life
Abstract
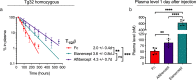
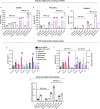
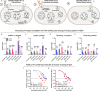
Antibody-based therapeutics (ABTs) are used to treat a range of diseases. Most ABTs are either full-length IgG1 antibodies or fusions between for instance antigen (Ag)-binding receptor domains and the IgG1 Fc fragment. Interestingly, their plasma half-life varies considerably, which may relate to how they engage the neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn). As such, there is a need for an in-depth understanding of how different features of ABTs affect FcRn-binding and transport behavior. Here, we report on how FcRn-engagement of the IgG1 Fc fragment compare to clinically relevant IgGs and receptor domain Fc fusions, binding to VEGF or TNF-α. The results reveal FcRn-dependent intracellular accumulation of the Fc, which is in line with shorter plasma half-life than that of full-length IgG1 in human FcRn-expressing mice. Receptor domain fusion to the Fc increases its half-life, but not to the extent of IgG1. This is mirrored by a reduced cellular recycling capacity of the Fc-fusions. In addition, binding of cognate Ag to ABTs show that complexes of similar size undergo cellular transport at different rates, which could be explained by the biophysical properties of each ABT. Thus, the study provides knowledge that should guide tailoring of ABTs regarding optimal cellular sorting and plasma half-life.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
M.C.M. has been a member of advisory boards at Bayer, Novartis, Roche and Allergan and has received lecture fees from Bayer and Roche. Ø.K.J. has been member of Bayer, Allergan and Roche advisory boards and has received lecture fees from Bayer and Allergan. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

