Integrating de novo and inherited variants in 42,607 autism cases identifies mutations in new moderate-risk genes
- PMID: 35982159
- PMCID: PMC9470534
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-022-01148-2
Integrating de novo and inherited variants in 42,607 autism cases identifies mutations in new moderate-risk genes
Abstract
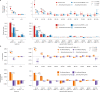
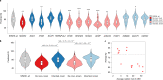
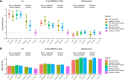
To capture the full spectrum of genetic risk for autism, we performed a two-stage analysis of rare de novo and inherited coding variants in 42,607 autism cases, including 35,130 new cases recruited online by SPARK. We identified 60 genes with exome-wide significance (P < 2.5 × 10-6), including five new risk genes (NAV3, ITSN1, MARK2, SCAF1 and HNRNPUL2). The association of NAV3 with autism risk is primarily driven by rare inherited loss-of-function (LoF) variants, with an estimated relative risk of 4, consistent with moderate effect. Autistic individuals with LoF variants in the four moderate-risk genes (NAV3, ITSN1, SCAF1 and HNRNPUL2; n = 95) have less cognitive impairment than 129 autistic individuals with LoF variants in highly penetrant genes (CHD8, SCN2A, ADNP, FOXP1 and SHANK3) (59% vs 88%, P = 1.9 × 10-6). Power calculations suggest that much larger numbers of autism cases are needed to identify additional moderate-risk genes.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
D.H.G. has received consulting fees or equity participation for scientific advisory board work from Ovid Therapeutics, Axial Biotherapeutics, Acurastem, and Falcon Computing. E.E.E. serves on the Scientific Advisory Board of Variant Bio. W.K.C. serves on Scientific Advisory Board of the Regeneron Genetics Center and is the Director of Clinical Research for SFARI. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures








References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 MH122491/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DC014489/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM139776/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM120609/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- K99 MH117165/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH105527/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD103537/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD103556/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008629/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD103525/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101221/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

