Persistent T-cell exhaustion in relation to prolonged pulmonary pathology and death after severe COVID-19: Results from two Norwegian cohort studies
- PMID: 35982589
- PMCID: PMC9805032
- DOI: 10.1111/joim.13549
Persistent T-cell exhaustion in relation to prolonged pulmonary pathology and death after severe COVID-19: Results from two Norwegian cohort studies
Abstract
Background: T-cell activation is associated with an adverse outcome in COVID-19, but whether T-cell activation and exhaustion relate to persistent respiratory dysfunction and death is unknown.
Objectives: To investigate whether T-cell activation and exhaustion persist and are associated with prolonged respiratory dysfunction and death after hospitalization for COVID-19.
Methods: Plasma and serum from two Norwegian cohorts of hospitalized patients with COVID-19 (n = 414) were analyzed for soluble (s) markers of T-cell activation (sCD25) and exhaustion (sTim-3) during hospitalization and follow-up.
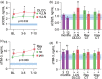
Results: Both markers were strongly associated with acute respiratory failure, but only sTim-3 was independently associated with 60-day mortality. Levels of sTim-3 remained elevated 3 and 12 months after hospitalization and were associated with pulmonary radiological pathology after 3 months.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest prolonged T-cell exhaustion is an important immunological sequela, potentially related to long-term outcomes after severe COVID-19.
Keywords: NOR-Solidarity; SARS-CoV-2; T-cell activation; T-cell exhaustion; pulmonary function.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Internal Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Association for Publication of The Journal of Internal Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Figures




References
-
- Klenerman P, Hill A. T cells and viral persistence: lessons from diverse infections. Nat Immunol. 2005;6:873–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

