This is a preprint.
Urine-based multi-omic comparative analysis of COVID-19 and bacterial sepsis-induced ARDS
- PMID: 35982662
- PMCID: PMC9387152
- DOI: 10.1101/2022.08.10.22277939
Urine-based multi-omic comparative analysis of COVID-19 and bacterial sepsis-induced ARDS
Update in
-
Urine-based multi-omic comparative analysis of COVID-19 and bacterial sepsis-induced ARDS.Mol Med. 2023 Jan 26;29(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s10020-023-00609-6. Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 36703108 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), a life-threatening condition during critical illness, is a common complication of COVID-19. It can originate from various disease etiologies, including severe infections, major injury, or inhalation of irritants. ARDS poses substantial clinical challenges due to a lack of etiology-specific therapies, multisystem involvement, and heterogeneous, poor patient outcomes. A molecular comparison of ARDS groups holds the potential to reveal common and distinct mechanisms underlying ARDS pathogenesis. In this study, we performed a comparative analysis of urine-based metabolomics and proteomics profiles from COVID-19 ARDS patients (n = 42) and bacterial sepsis-induced ARDS patients (n = 17). The comparison of these ARDS etiologies identified 150 metabolites and 70 proteins that were differentially abundant between the two groups. Based on these findings, we interrogated the interplay of cell adhesion/extracellular matrix molecules, inflammation, and mitochondrial dysfunction in ARDS pathogenesis through a multi-omic network approach. Moreover, we identified a proteomic signature associated with mortality in COVID-19 ARDS patients, which contained several proteins that had previously been implicated in clinical manifestations frequently linked with ARDS pathogenesis. In summary, our results provide evidence for significant molecular differences in ARDS patients from different etiologies and a potential synergy of extracellular matrix molecules, inflammation, and mitochondrial dysfunction in ARDS pathogenesis. The proteomic mortality signature should be further investigated in future studies to develop prediction models for COVID-19 patient outcomes.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
A.M.K.C. is a cofounder and equity stockholder for Proterris, which develops therapeutic uses for carbon monoxide. A.M.K.C. has a use patent on CO. Additionally, A.M.K.C. has a patent in COPD. ES consults for Axle informatics regarding COVID vaccine clinical trials through NIAID. JK holds equity in Chymia LLC and IP in PsyProtix and is cofounder of iollo.
Figures

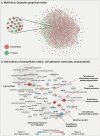

References
-
- UNDP. Everyone Included: Social Impact of COVID-19 | DISD. United Nations; https://www.un.org/development/desa/dspd/everyone-included-covid-19.html.
-
- Chriscaden Kimberly. Impact of COVID-19 on people’s livelihoods, their health and our food systems. World Health Organization; 4–7 https://www.who.int/news/item/13-10-2020-impact-of-covid-19-on-people’s-... (2020).
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
