Ion absorption, distribution and salt tolerance threshold of three willow species under salt stress
- PMID: 35982705
- PMCID: PMC9379094
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.969896
Ion absorption, distribution and salt tolerance threshold of three willow species under salt stress
Abstract
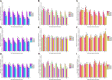
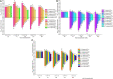
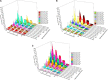
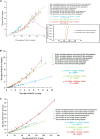
To investigate the response mechanism and salt tolerance threshold of three willow seedlings (Salix matsudana, Salix gordejevii, Salix linearistipularis), the absorption, transport and distribution of salt ions (Na+, K+, Ca2+) were studied under hydroponic conditions with different salt concentrations (CK, 171, 342, 513, and 684 mm) and treatment times (1, 3, 5, 8, 11, and 15 days). Salix linearistipularis has the weakest ability to maintain its apparent shape, while Salix matsudana has the strongest ability. The three plants have a certain Na+ interception ability, and the interception abilities of Salix matsudana and Salix gordejevii are higher than that of Salix linearistipularis. The leaf S AK,Na of Salix linearistipularis were higher than those of Salix matsudana and Salix gordejevii. The leaf selection ability was the highest, and the selection ability of the root system was the lowest in Salix linearistipularis. The long-term low salt concentration and the short-term high salt concentration can increase the root and leaf salinity. Salix matsudana grows more stably in a long-term high-salt stress environment, and Salix gordejevii grows stably in a short-term high-salt stress environment. However, Salix linearistipularis is more suitable for planting as an indicative plant because of its sensitivity to salt stress. The root Na+ content of Salix matsudana and Salix gordejevii was 34.21 mg/g, which was the maximum root retention capacity. Once the accumulation of Na+ content in roots exceeds this value, the rejection capacity of roots is broken through, and the selective ion absorption capacity will rapidly become weak, which easily leads to the death of plants.
Keywords: NaCl stress; Salix gordejevii; Salix linearistipularis; Salix matsudana; ion absorption; salt tolerance mechanism; threshold; transport and distribution.
Copyright © 2022 Ran, Huang, Wang, Liang, Wang, Li, Huo, Liu and Ma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Aghaleh M., Niknam V., Ebrahimzadeh H., Razavi K. (2011). Effect of salt stress on physiological and antioxidative responses in two species of Salicornia (S. persica and S. europaea). Acta Physiol. Plant. 33 1261–1270. 10.1007/s11738-010-0656-x - DOI
-
- Altaf M. A., Shahid R., Ren M. X., Altaf M. M., Khan L. U., Shahid S., et al. (2021). Melatonin alleviates salt damage in tomato seedling: a root architecture system, photosynthetic capacity, ion homeostasis, and antioxidant enzymes analysis. Sci. Hortic. 285:110145. 10.1016/j.scienta.2021.110145 - DOI
-
- Ayars J. E., Christen E. W., Hornbuckle J. W. (2006). Controlled drainage for improved water management in arid regions irrigated agriculture. Agric. Water Manag. 86 128–139. 10.1016/j.agwat.2006.07.004 - DOI
-
- Banakar M. H., Amiri H., Ardakani M. R. S., Ranjbar G. H. (2022). Susceptibility and tolerance of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graceum L.) to salt stress: physiological and biochemical inspections. Environ. Exp. Bot. 194:104748. 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2021.104748 - DOI
-
- Bian A. N., Lu L. M. (2022). Mechanism of physiological difference in response to substrate salinity and salt spray of Barringtoniaracemosa seedlings. Plant Physiol. J. 58, 415–424. Available online at: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?FileName=ZWSL202202019&DbNa...
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

