Personalised 3D printed respirators for healthcare workers during the COVID-19 pandemic
- PMID: 35982716
- PMCID: PMC9380470
- DOI: 10.3389/fmedt.2022.963541
Personalised 3D printed respirators for healthcare workers during the COVID-19 pandemic
Abstract
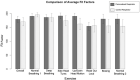
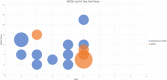
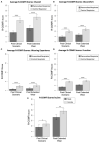
Widespread issues in respirator availability and fit have been rendered acutely apparent by the COVID-19 pandemic. This study sought to determine whether personalized 3D printed respirators provide adequate filtration and function for healthcare workers through a Randomized Controlled Trial (RCT). Fifty healthcare workers recruited within NHS Lothian, Scotland, underwent 3D facial scanning or 3D photographic reconstruction to produce 3D printed personalized respirators. The primary outcome measure was quantitative fit-testing to FFP3 standard. Secondary measures included respirator comfort, wearing experience, and function instrument (R-COMFI) for tolerability, Modified Rhyme Test (MRT) for intelligibility, and viral decontamination on respirator material. Of the 50 participants, 44 passed the fit test with the customized respirator, not significantly different from the 38 with the control (p = 0.21). The customized respirator had significantly improved comfort over the control respirator in both simulated clinical conditions (p < 0.0001) and during longer wear (p < 0.0001). For speech intelligibility, both respirators performed equally. Standard NHS decontamination agents were able to eradicate 99.9% of viral infectivity from the 3D printed plastics tested. Personalized 3D printed respirators performed to the same level as control disposable FFP3 respirators, with clear communication and with increased comfort, wearing experience, and function. The materials used were easily decontaminated of viral infectivity and would be applicable for sustainable and reusable respirators.
Keywords: 3D printing; COVID-19; PPE; facemask; fit-testing.
Copyright © 2022 Roche, McConnell, Donaldson, Lawson, Tan, Toft, Cairns, Colle, Coleman, Stewart, Digard, Norrie and Stokes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- WHO . Infection Prevention and Control of Epidemic- and Pandemic-Prone Acute Respiratory Infections in Health Care. Annex A, Respiratory Infection. Geneva: World Health Organization; (2014). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

