Immunotherapy in the Treatment of Platinum-Resistant Ovarian Cancer: Current Perspectives
- PMID: 35982728
- PMCID: PMC9379118
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S335936
Immunotherapy in the Treatment of Platinum-Resistant Ovarian Cancer: Current Perspectives
Abstract
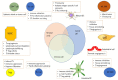
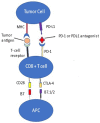
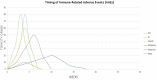
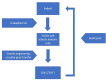
Epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) is the most lethal gynecologic cancer. The gold standard therapeutic approach is a combination of surgery plus chemotherapy. Unfortunately, 80% of patients with EOC suffer recurrence within 2-years and the overall response rate for platinum-resistant epithelial ovarian cancer to cytotoxic chemotherapy or poly-(adenosine diphosphate)-ribose polymerase (PARP) inhibitor is modest. New therapies are needed to improve overall survival. The role of immunotherapy has been established in endometrial and cervical cancers, however its effective use in EOC has been limited due to the intrinsic genomics and micro-immune environment associated with EOC. Studies evaluating immunotherapy, largely immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI), have shown limited activity, yet some patients benefit greatly. Thus, significant efforts must be devoted to finding new strategies for the use of immunotherapy/immunomodulatory drugs (IMiDs). Immunotherapy has a well-tolerated safety profile; however, cost-effectiveness can be an obstacle. The aim of this article is to review the most recent research into the use of IMiDs in patients with platinum-resistant epithelial ovarian cancer.
Keywords: adverse events; immune checkpoint inhibitors; immunotherapy; ovarian cancer; platinum-resistant; recurrent.
© 2022 Awada et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Nathalie D McKenzie reports advisory board and/or speaker fees from GSK, Merck, Clovis, and AstraZeneca, outside the submitted work. Prof. Dr. Robert W Holloway reports personal fees from Eisai, outside the submitted work. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

