Acute ischemic stroke treatment model for Poland in the mechanical thrombectomy era - which way to go?
- PMID: 35982743
- PMCID: PMC9199023
- DOI: 10.5114/aic.2022.115269
Acute ischemic stroke treatment model for Poland in the mechanical thrombectomy era - which way to go?
Abstract
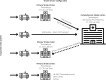
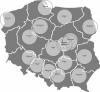
The interventional treatment of acute ischemic stroke with large vessel occlusion has revolutionized patient care in recent years. The Mechanical Thrombectomy Pilot Program in Poland is due to end soon. It seems the right time to summarize the achievements and name the problems of a centralized stroke care system and decide what future model of treatment and transportation to implement. In order to provide the best care for our patients, it is crucial to establish the actual needs in stroke and tailor the mechanical thrombectomy system structure accordingly. The analysis of data from well-organized health systems in the world suggests that to deliver adequate numbers of mechanical thrombectomy to stroke patients in Poland, we would need to at least double the number of procedures currently performed. To achieve this, an essential system reorganization and adjustments are required, with special emphasis on the number of mechanical thrombectomy centers and transportation models. The strengths and weaknesses of two dominant transportation models (mothership and drip-and-ship) are herein discussed, and a proposal on how to build an efficient and cost-effective mechanical thrombectomy stroke network in Poland is put forward. The article is an invitation to open an interdisciplinary discussion on the best treatment model of acute ischemic stroke patients requiring mechanical thrombectomy in Poland.
Keywords: acute ischemic stroke; mechanical thrombectomy; stroke network modeling; stroke transportation model; thrombectomy-capable stroke center.
Copyright: © 2022 Termedia Sp. z o. o.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Berkhemer OA, Fransen PS, Beumer D, et al. . MR CLEAN Investigators . A randomized trial of intraarterial treatment for acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 2015; 372: 11-20. - PubMed
-
- Campbell BC, Mitchell PJ, Kleinig TJ, et al. . EXTEND-IA Investigators . Endovascular therapy for ischemic stroke with perfusion-imaging selection. N Engl J Med 2015; 372: 1009-18. - PubMed
-
- Jovin TG, Chamorro A, Cobo E, et al. . REVASCAT Trial Investigators . Thrombectomy within 8 hours after symptom onset in ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 2015; 372: 2296-306. - PubMed
-
- Goyal M, Demchuk AM, Menon BK, et al. . ESCAPE Trial Investigators . Randomized assessment of rapid endovascular treatment of ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 2015; 372: 1019-30. - PubMed
-
- Saver JL, Goyal M, Bonafe Aet al. . Stent-retriever thrombectomy after intravenous t-PA vs. t-PA alone in stroke. N Engl J Med 2015; 372: 2285-95. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
