Real-World Evaluation of Clinical Response and Long-Term Healthcare Resource Utilization Patterns Following Treatment with a Digital Therapeutic for Chronic Insomnia
- PMID: 35983014
- PMCID: PMC9379126
- DOI: 10.2147/CEOR.S368780
Real-World Evaluation of Clinical Response and Long-Term Healthcare Resource Utilization Patterns Following Treatment with a Digital Therapeutic for Chronic Insomnia
Abstract
Background and objectives: This analysis evaluated insomnia severity and long-term impact on healthcare resource utilization (HCRU) and costs after treatment with Somryst® (previously called SHUTi), a digital therapeutic delivering cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I).
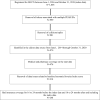
Methods: Change from baseline in insomnia severity index (ISI) score was assessed using last observed ISI score. A pre/post analysis of claims data was conducted, comparing HCRU in patients with self-identified sleep problems who successfully initiated the therapeutic (index date) between June 1, 2016 and December 31, 2018.
Results: A total of 248 patients were analyzed (median age 56.5 years, 57.3% female, mean ISI score 19.13, 52.4% treated with sleep aid medications pre-index). After 9 weeks, mean ISI score declined by 37.2% from baseline (19.1 vs 12.0), 58.8% of patients achieved ISI responder status (ISI score improved by =>7; NNT: 1.7), and 26.6% of patients achieved insomnia remission (ISI score <8; NNT for remission: 3.8). After two-year follow-up, post-index events were reduced (compared to 2 years pre-index) for emergency department visits (-53%; IRR: 0.47; 95% CI 0.27, 0.82; P=0.008), hospiatizations (-21%; IRR: 0.79; 95% CI 0.46, 1.35; P=0.389) and hospital outpatient visits (-13%; IRR: 0.87; 95% CI 0.66, 1.14; P=0.315). Slightly increased rates were observed for ambulatory surgical center visits (2%; IRR: 1.02; 95% CI 0.73, 1.44; P=0.903) and office visits (2%; IRR: 1.02; 95% CI 0.92, 1.14; P=0.672). The number of patients treated with sleep aid medications dropped 18.5% (52.4% pre-index vs 42.7% post-index). Average number of prescriptions decreased from 3.98 pre-index to 3.73 post-index (P= 0.552). Total two-year cost reduction post-index vs pre-index was $510,678, or -$2059 per patient.
Conclusion: In a real-world cohort of patients with chronic insomnia, treatment with a digital therapeutic delivering CBT-I was associated with reductions in insomnia severity, emergency department visits, and net costs.
Keywords: CBT-I; SHUTi; Somryst; chronic insomnia; cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia; prescription digital therapeutic.
© 2022 Forma et al.
Conflict of interest statement
FF, FPT, XX, FFV, and YAM are employees of Pear Therapeutics (US), Inc. FPT also reports equity and employment from BeHealth Solutions, during the conduct of the study; and was a previous faculty member at institution (University of Virginia) that developed precursor (SHUTi) to this work. TGK and RB are employees of Market Access Consulting, Labcorp Drug Development, which participated in this study under contract with Pear Therapeutics (US), Inc. DCM is a consultant of Strategic Therapeutics, LLC, which participated in this study under contract with Pear Therapeutics (US), Inc. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources