Neural Network Model for Perceptual Evaluation of Product Modelling Design Based on Multimodal Image Recognition
- PMID: 35983136
- PMCID: PMC9381256
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/1665021
Neural Network Model for Perceptual Evaluation of Product Modelling Design Based on Multimodal Image Recognition
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Neural Network Model for Perceptual Evaluation of Product Modelling Design Based on Multimodal Image Recognition.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2023 Oct 18;2023:9843472. doi: 10.1155/2023/9843472. eCollection 2023. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37886374 Free PMC article.
Abstract
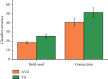
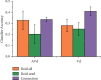
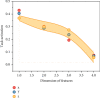
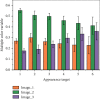
With the homogenization of product function and performance, the design technology for product appearance quality has been increasingly valued by academia and industry and has become an effective technical way to meet the continuously growing diversified and personalized needs of consumers. The appearance quality attribute of a product can be characterized or described by its appearance image. Data-driven product appearance image design is based on the quantitative data of product appearance and consumer emotional needs and completes the product appearance through computer-aided design technology and intelligent algorithms. Design innovation can help companies quickly respond to consumers' emotional needs and effectively improve design quality and product competitiveness. When visual objects are disturbed in complex scenes, the issues such as how the human brain coordinates multisensory information processing and what neural processing mechanisms follow are still unclear. In this paper, a visual object recognition experiment in a complex scene was designed and the brain activation signals of three modalities of noise, added audio-visual (AVd), single visual noise and noise (Vd), and single-audio (A), were recorded. The properties and neural processing mechanisms of multisensory modulation of auditory stimuli during noisy image recognition were explored. Using the conjunction method combined with the classic "max criterion" rule, it was found that only when a certain amount of noise was added to the visual stimulus, the integration area changed. The product appearance has a decisive influence on the user's product perceptual attribute preference and greatly affects the consumer's satisfaction. The importance of product appearance image design is increasingly prominent. In addition, pattern analysis of brain activation signals confirmed that semantically consistent sounds can facilitate the recognition of noisy images and this facilitation shows a certain category selectivity when subdivided into categories. Using the analysis method of functional connectivity, a functional connectivity network containing nodes at different integration levels was constructed to explore the overall characteristics and processing patterns of the multisensory network. Through the analysis of the network connection relationship, it is found that the prefrontal cortex, STS, and lateral occipital lobe are the nodes with more aggregation in the network, and their functions are similar to the hub in the network. The brain functional network was constructed, and functional connectivity was used to explore the connection characteristics of the network and the multisensory modulation mechanism between different processing levels of the brain.
Copyright © 2022 Jie Wu and Long Jia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Distinct functional contributions of primary sensory and association areas to audiovisual integration in object categorization.J Neurosci. 2010 Feb 17;30(7):2662-75. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5091-09.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20164350 Free PMC article.
-
Revealing the multisensory modulation of auditory stimulus in degraded visual object recognition by dynamic causal modeling.Brain Imaging Behav. 2020 Aug;14(4):1187-1198. doi: 10.1007/s11682-019-00134-3. Brain Imaging Behav. 2020. PMID: 31172360
-
Constructing scenes from objects in human occipitotemporal cortex.Nat Neurosci. 2011 Sep 4;14(10):1323-9. doi: 10.1038/nn.2903. Nat Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21892156 Free PMC article.
-
Visual Object Recognition: Do We (Finally) Know More Now Than We Did?Annu Rev Vis Sci. 2016 Oct 14;2:377-396. doi: 10.1146/annurev-vision-111815-114621. Epub 2016 Aug 3. Annu Rev Vis Sci. 2016. PMID: 28532357 Review.
-
Top-down facilitation of visual object recognition: object-based and context-based contributions.Prog Brain Res. 2006;155:3-21. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(06)55001-0. Prog Brain Res. 2006. PMID: 17027376 Review.
Cited by
-
Retracted: Neural Network Model for Perceptual Evaluation of Product Modelling Design Based on Multimodal Image Recognition.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2023 Oct 18;2023:9843472. doi: 10.1155/2023/9843472. eCollection 2023. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37886374 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hammad M., Liu Y., Wang K. Multimodal biometric authentication systems using convolution neural network based on different level fusion of ECG and f. IEEE Access . 2019;7:26527–26542. doi: 10.1109/access.2018.2886573. - DOI
-
- Holzinger A., Malle B., Saranti A., Pfeifer B. Towards multi-modal causability with Graph Neural Networks enabling information fusion for explainable AI. Information Fusion . 2021;71:28–37. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2021.01.008. - DOI
-
- Hu C., Wang Y. An efficient convolutional neural network model based on object-level attention mechanism for casting defect detection on radiography images. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics . 2020;67(12):10922–10930. doi: 10.1109/tie.2019.2962437. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

