Driving mechanism of subjective cognition on farmers' adoption behavior of straw returning technology: Evidence from rice and wheat producing provinces in China
- PMID: 35983208
- PMCID: PMC9379131
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.922889
Driving mechanism of subjective cognition on farmers' adoption behavior of straw returning technology: Evidence from rice and wheat producing provinces in China
Abstract
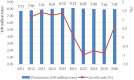
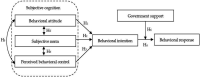
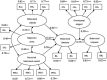
Straw burning is one of the important causes of environmental pollution in rural China. As an important green production technology, straw returning is beneficial to the improvement of rural environment and the sustainable development of agriculture. Based on the improved planned behavior theory, taking the survey data of 788 farmers in Shandong, Henan, Hubei, and Hunan provinces as samples, this paper uses a multi-group structural equation model to explore the driving mechanism of subjective cognition on the adoption behavior of farmers' straw returning technology. The results show that behavioral attitude, subjective norm, and perceived behavioral control, which represent subjective cognition, all have significant driving effects on farmers' intention to adopt straw returning technology. Behavioral intention plays a mediating role in the process of subjective cognition driving farmers' adoption behavior of straw returning technology. Government support has a moderating role in the path from farmers' behavioral intention to behavioral response. The subjective cognition of different types of farmers has a significant driving effect on the adoption intention of straw returning technology, but the driving strength weakens with the increase of the degree of farmers' concurrent occupation. This study provides guidance for improving the government's straw returning policy and regulating straw returning behavior.
Keywords: SEM; TPB; straw returning; straw returning technology; subjective cognition.
Copyright © 2022 Ren and Zhong.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

