Prostate Cancer Therapy Using Docetaxel and Formononetin Combination: Hyaluronic Acid and Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Targeted Peptide Dual Ligands Modified Binary Nanoparticles to Facilitate the in vivo Anti-Tumor Activity
- PMID: 35983428
- PMCID: PMC9380734
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S366622
Prostate Cancer Therapy Using Docetaxel and Formononetin Combination: Hyaluronic Acid and Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Targeted Peptide Dual Ligands Modified Binary Nanoparticles to Facilitate the in vivo Anti-Tumor Activity
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the prostate cancer therapy efficiency of the synergistic combination docetaxel (DTX) and formononetin (FMN) in one nano-sized drug delivery system. Hyaluronic acid (HA) and epidermal growth factor receptor-targeted peptide (GE11) dual ligands were applied to modify the nano-systems.
Methods: In this study, GE11-modified nanoparticles (GE-NPs) were applied for the loading of DTX, and HA-decorated NPs (HA-NPs) were used to encapsulate FMN. HA and GE11 dual ligand-modified binary nanoparticles (HAGE-DTX/FMN-NPs) were constructed by the self-assembling of GE-NPs and HA-NPs. The anti-PCa ability of the system was evaluated in vitro on PC-3 human prostate carcinoma cells (PC3 cells) and in vivo on PC3 tumor-bearing mice in comparison with single NPs and free drugs formulations.
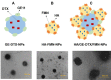
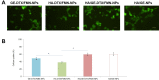
Results: HA/GE-DTX/FMN-NPs were nano-sized particles with smaller particles coating on the inner core and achieved a size of 189.5 nm. HA/GE-DTX/FMN-NPs showed a cellular uptake efficiency of 59.6%, and a more efficient inhibition effect on PC3 cells compared with single ligand-modified NPs and free drugs. HA/GE-DTX/FMN-NPs showed significantly higher tumor inhibition efficiency than their single drug-loaded counterparts and free drugs.
Conclusion: HA/GE-DTX/FMN-NPs have a synergistic anti-tumor effect and also could the reduce unexpected side effects during the cancer therapy. It could be used as a promising anti-PCa system.
Keywords: binary nanoparticles; docetaxel; epidermal growth factor receptor; formononetin; hyaluronic acid; prostate cancer.
© 2022 Dong et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures





References
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network: NCCN clinical prastice guidelines in oncology (NCCN Guidelines®): prostate cancer V.2.2021. National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc. Available from: https://www.nccn.org/guidelines/guidelines-detail?category=1&id=1459. Accessed July 29, 2022.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

