A Framework and Blueprint for Building Capacity in Global Orthopaedic Surgical Outreach
- PMID: 35984012
- PMCID: PMC10760412
- DOI: 10.2106/JBJS.22.00353
A Framework and Blueprint for Building Capacity in Global Orthopaedic Surgical Outreach
Abstract
Background: Nongovernmental organizations (NGOs) from high-income countries provide surgical outreach for patients in low and middle-income countries (LMICs); however, these efforts lack a coordinated measurement of their ability to build capacity. While the World Health Organization and others recommend outreach trips that aim to build the capacity of the local health-care system, no guidance exists on how to accomplish this. The objective of this paper is to establish a framework and a blueprint to guide the operations of NGOs that provide outreach to build orthopaedic surgical capacity in LMICs.
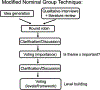
Methods: We conducted a qualitative analysis of semistructured interviews with 16 orthopaedic surgeons and administrators located in 7 countries (6 LMICs) on the necessary domains for capacity-building; the analysis was guided by a literature review of capacity-building frameworks. We subsequently conducted a modified nominal group technique with a consortium of 10 U.S.-based surgeons with expertise in global surgical outreach, which was member-checked with 8 new stakeholders from 4 LMICs.
Results: A framework with 7 domains for capacity-building in global surgical outreach was identified. The domains included professional development, finance, partnerships, governance, community impact, culture, and coordination. These domains were tiered in a hierarchical system to stratify the level of capacity for each domain. A blueprint was developed to guide the operations of an organization seeking to build capacity.
Conclusions: The developed framework identified 7 domains to address when building capacity during global orthopaedic surgical outreach. The framework and its tiered system can be used to assess capacity and guide capacity-building efforts in LMICs. The developed blueprint can inform the operations of NGOs toward activities that focus on building capacity in order to ensure a measured and sustained impact.
Copyright © 2022 by The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery, Incorporated.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: The Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest forms are provided with the online version of the article ( http://links.lww.com/JBJS/H185 ).
Figures


References
-
- Lim SS, Vos T, Flaxman AD, et al. A comparative risk assessment of burden of disease and injury attributable to 67 risk factors and risk factor clusters in 21 regions, 1990–2010:a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380(9859):2224–2260. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61766-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Injuries and violence: key facts. World Health Organization; https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/injuries-and-violence (accessed 25 June 2022).

