Dysregulation of the hippocampal neuronal network by LGI1 auto-antibodies
- PMID: 35984846
- PMCID: PMC9390894
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0272277
Dysregulation of the hippocampal neuronal network by LGI1 auto-antibodies
Abstract
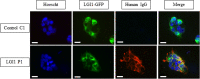
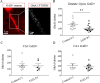
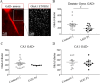
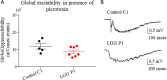
LGI1 is a neuronal secreted protein highly expressed in the hippocampus. Epileptic seizures and LGI1 hypo-functions have been found in both ADLTE, a genetic epileptogenic syndrome and LGI1 limbic encephalitis (LE), an autoimmune disease. Studies, based mainly on transgenic mouse models, investigated the function of LGI1 in the CNS and strangely showed that LGI1 loss of function, led to a decreased AMPA-receptors (AMPA-R) expression. Our project intends at better understanding how an altered function of LGI1 leads to epileptic seizures. To reach our goal, we infused mice with LGI1 IgG purified from the serum of patients diagnozed with LGI1 LE. Super resolution imaging revealed that LGI1 IgG reduced AMPA-R expression at the surface of inhibitory and excitatory neurons only in the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus. Complementary electrophysiological approaches indicated that despite reduced AMPA-R expression, LGI1 IgG increased the global hyperexcitability in the hippocampal neuronal network. Decreased AMPA-R expression at inhibitory neurons and the lack of LGI1 IgG effect in presence of GABA antagonist on excitability, led us to conclude that LGI1 function might be essential for the proper functioning of the overall network and orchestrate the imbalance between inhibition and excitation. Our work suggests that LGI1 IgG reduced the inhibitory network activity more significantly than the excitatory network shedding lights on the essential role of the inhibitory network to trigger epileptic seizures in patients with LGI1 LE.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Irani SR, Alexander S, Waters P, Kleopa KA, Pettingill P, Zuliani L, et al. Antibodies to Kv1 potassium channel-complex proteins leucine-rich, glioma inactivated 1 protein and contactin-associated protein-2 in limbic encephalitis, Morvan’s syndrome and acquired neuromyotonia. Brain. 2010. Sep;133(9):2734–48. doi: 10.1093/brain/awq213 - DOI - PMC - PubMed

