A highly selective JAK3 inhibitor is developed for treating rheumatoid arthritis by suppressing γc cytokine-related JAK-STAT signal
- PMID: 35984890
- PMCID: PMC9390995
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abo4363
A highly selective JAK3 inhibitor is developed for treating rheumatoid arthritis by suppressing γc cytokine-related JAK-STAT signal
Abstract
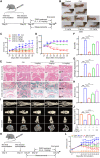
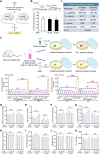
Janus kinases (JAKs) play a critical role in immune responses by relaying signals from more than 50 cytokines, making them attractive therapeutic targets for autoimmune diseases. Although approved JAK inhibitors have demonstrated clinical efficacy, they target a broad spectrum of cytokines, which results in side effects. Therefore, next-generation inhibitors maintain efficacy, while sparing adverse events need to be developed. Among members of the JAK family, JAK3 only regulates a narrow spectrum of γc cytokines and becomes a potentially ideal target. Here, a highly JAK3-selective inhibitor Z583 is developed, which showed a potent inhibition of JAK3 with an IC50 of 0.1 nM and exhibited a 4500-fold selectivity for JAK3 than other JAK subtypes. Furthermore, Z583 completely inhibited the γc cytokine signaling and sufficiently blocked the development of inflammatory response in RA model, while sparing hematopoiesis. Collectively, the highly selective JAK3 inhibitor Z583 is a promising candidate with significant therapeutic potential for autoimmune diseases.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Structural optimizations on the 7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine scaffold to develop highly selective, safe and potent JAK3 inhibitors for the treatment of Rheumatoid arthritis.Bioorg Chem. 2024 Aug;149:107499. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2024.107499. Epub 2024 May 25. Bioorg Chem. 2024. PMID: 38815476
-
Design and Synthesis of a Highly Selective JAK3 Inhibitor for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis.Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2017 Nov;350(11). doi: 10.1002/ardp.201700194. Epub 2017 Sep 25. Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2017. PMID: 28944566
-
Design, synthesis, and pharmacological evaluation of 4- or 6-phenyl-pyrimidine derivatives as novel and selective Janus kinase 3 inhibitors.Eur J Med Chem. 2020 Apr 1;191:112148. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112148. Epub 2020 Feb 16. Eur J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32097841
-
The role of the JAK/STAT signal pathway in rheumatoid arthritis.Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2018 Jun;10(5-6):117-127. doi: 10.1177/1759720X18776224. Epub 2018 May 19. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2018. PMID: 29942363 Free PMC article. Review.
-
JAK3 inhibitors for the treatment of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases: a patent review (2016-present).Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2022 Mar;32(3):225-242. doi: 10.1080/13543776.2022.2023129. Epub 2022 Jan 6. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2022. PMID: 34949146 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of bone homeostasis: signaling pathways and therapeutic targets.MedComm (2020). 2024 Jul 24;5(8):e657. doi: 10.1002/mco2.657. eCollection 2024 Aug. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 39049966 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bone-derived MSCs encapsulated in alginate hydrogel prevent collagen-induced arthritis in mice through the activation of adenosine A2A/2B receptors in tolerogenic dendritic cells.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023 Jun;13(6):2778-2794. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.04.003. Epub 2023 Apr 7. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023. PMID: 37425054 Free PMC article.
-
Computational 3D Modeling-Based Identification of Inhibitors Targeting Cysteine Covalent Bond Catalysts for JAK3 and CYP3A4 Enzymes in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis.Molecules. 2023 Dec 19;29(1):23. doi: 10.3390/molecules29010023. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38202604 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms and therapeutic prospect of the JAK-STAT signaling pathway in liver cancer.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 Jan;480(1):1-17. doi: 10.1007/s11010-024-04983-5. Epub 2024 Mar 22. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 38519710 Review.
-
IRG1/Itaconate inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of CD69+CD103+CD8+ tissue-resident memory T cells in autoimmune hepatitis by regulating the JAK3/STAT3/P53 signalling pathway.Apoptosis. 2024 Oct;29(9-10):1738-1756. doi: 10.1007/s10495-024-01970-5. Epub 2024 Apr 19. Apoptosis. 2024. PMID: 38641760
References
-
- Smolen J. S., Steiner G., Therapeutic strategies for rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2, 473–488 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Smolen J. S., Landewe R., Bijlsma J., Burmester G., Chatzidionysiou K., Dougados M., Nam J., Ramiro S., Voshaar M., van Vollenhoven R., Aletaha D., Aringer M., Boers M., Buckley C. D., Buttgereit F., Bykerk V., Cardiel M., Combe B., Cutolo M., van Eijk-Hustings Y., Emery P., Finckh A., Gabay C., Gomez-Reino J., Gossec L., Gottenberg J. E., Hazes J. M. W., Huizinga T., Jani M., Karateev D., Kouloumas M., Kvien T., Li Z. G., Mariette X., McInnes I., Mysler E., Nash P., Pavelka K., Poor G., Richez C., van Riel P., Rubbert-Roth A., Saag K., da Silva J., Stamm T., Takeuchi T., Westhovens R., de Wit M., van der Heijde D., EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2016 update. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 76, 960–970 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Singh J. A., Saag K. G., Jr Bridges S. L., Akl E. A., Bannuru R. R., Sullivan M. C., Vaysbrot E., McNaughton C., Osani M., Shmerling R. H., Curtis J. R., Furst D. E., Parks D., Kavanaugh A., O’Dell J., King C., Leong A., Matteson E. L., Schousboe J. T., Drevlow B., Ginsberg S., Grober J., Clair E. W. S., Tindall E., Miller A. S., McAlindon T., 2015 American college of rheumatology guideline for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 68, 1–26 (2016). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

