Brain entropy, fractal dimensions and predictability: A review of complexity measures for EEG in healthy and neuropsychiatric populations
- PMID: 35985344
- PMCID: PMC9826422
- DOI: 10.1111/ejn.15800
Brain entropy, fractal dimensions and predictability: A review of complexity measures for EEG in healthy and neuropsychiatric populations
Abstract
There has been an increasing trend towards the use of complexity analysis in quantifying neural activity measured by electroencephalography (EEG) signals. On top of revealing complex neuronal processes of the brain that may not be possible with linear approaches, EEG complexity measures have also demonstrated their potential as biomarkers of psychopathology such as depression and schizophrenia. Unfortunately, the opacity of algorithms and descriptions originating from mathematical concepts have made it difficult to understand what complexity is and how to draw consistent conclusions when applied within psychology and neuropsychiatry research. In this review, we provide an overview and entry-level explanation of existing EEG complexity measures, which can be broadly categorized as measures of predictability and regularity. We then synthesize complexity findings across different areas of psychological science, namely, in consciousness research, mood and anxiety disorders, schizophrenia, neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative disorders, as well as changes across the lifespan, while addressing some theoretical and methodological issues underlying the discrepancies in the data. Finally, we present important considerations when choosing and interpreting these metrics.
Keywords: EEG; complexity; entropy; fractal dimension; psychopathology.
© 2022 The Authors. European Journal of Neuroscience published by Federation of European Neuroscience Societies and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
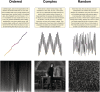
Figures
References
-
- Abasolo, D. , Hornero, R. , Gomez, C. , Garcia, M. , & Lopez, M. (2006). Analysis of EEG background activity in Alzheimer's disease patients with Lempel–Ziv complexity and central tendency measure. Medical Engineering & Physics, 28(4), 315–322. - PubMed
-
- Accardo, A. , Affinito, M. , Carrozzi, M. , & Bouquet, F. (1997). Use of the fractal dimension for the analysis of electroencephalographic time series. Biological Cybernetics, 77(5), 339–350. - PubMed
-
- Acharya, R. , Faust, O. , Kannathal, N. , Chua, T. , & Laxminarayan, S. (2005). Non‐linear analysis of EEG signals at various sleep stages. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 80(1), 37–45. - PubMed
-
- Acharya, R. , Fujita, H. , Sudarshan, V. K. , Ghista, D. N. , Lim, W. J. E. , & Koh, J. E. (2015). Automated prediction of sudden cardiac death risk using Kolmogorov complexity and recurrence quantification analysis features extracted from HRV signals. In 2015 IEEE international conference on systems, man, and cybernetics (pp. 1110–1115). IEEE.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

