HER2-enriched subtype and novel molecular subgroups drive aromatase inhibitor resistance and an increased risk of relapse in early ER+/HER2+ breast cancer
- PMID: 35985932
- PMCID: PMC9482930
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.104205
HER2-enriched subtype and novel molecular subgroups drive aromatase inhibitor resistance and an increased risk of relapse in early ER+/HER2+ breast cancer
Abstract
Background: Oestrogen receptor positive/ human epidermal growth factor receptor positive (ER+/HER2+) breast cancers (BCs) are less responsive to endocrine therapy than ER+/HER2- tumours. Mechanisms underpinning the differential behaviour of ER+HER2+ tumours are poorly characterised. Our aim was to identify biomarkers of response to 2 weeks' presurgical AI treatment in ER+/HER2+ BCs.
Methods: All available ER+/HER2+ BC baseline tumours (n=342) in the POETIC trial were gene expression profiled using BC360™ (NanoString) covering intrinsic subtypes and 46 key biological signatures. Early response to AI was assessed by changes in Ki67 expression and residual Ki67 at 2 weeks (Ki672wk). Time-To-Recurrence (TTR) was estimated using Kaplan-Meier methods and Cox models adjusted for standard clinicopathological variables. New molecular subgroups (MS) were identified using consensus clustering.
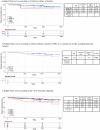
Findings: HER2-enriched (HER2-E) subtype BCs (44.7% of the total) showed poorer Ki67 response and higher Ki672wk (p<0.0001) than non-HER2-E BCs. High expression of ERBB2 expression, homologous recombination deficiency (HRD) and TP53 mutational score were associated with poor response and immune-related signatures with High Ki672wk. Five new MS that were associated with differential response to AI were identified. HER2-E had significantly poorer TTR compared to Luminal BCs (HR 2.55, 95% CI 1.14-5.69; p=0.0222). The new MS were independent predictors of TTR, adding significant value beyond intrinsic subtypes.
Interpretation: Our results show HER2-E as a standardised biomarker associated with poor response to AI and worse outcome in ER+/HER2+. HRD, TP53 mutational score and immune-tumour tolerance are predictive biomarkers for poor response to AI. Lastly, novel MS identify additional non-HER2-E tumours not responding to AI with an increased risk of relapse.
Funding: Cancer Research UK (CRUK/07/015).
Keywords: Aromatase inhibitors; Breast cancer; HER2+; HER2-Enriched subtype.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests MB reports grants from Fundacion Alonso Martin Escudero and has a patent filed for the novel molecular subgroups identified in this paper. ELK has a patent filed for the novel molecular subgroups identified in this paper. HT and LK report grants from Cancer Research UK, during the conduct of the study. JMB reports grants from Cancer Research UK, during the conduct of the study; grants and non-financial support from AstraZeneca, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Puma Biotechnology, Clovis Oncology, Pfizer, Janssen-Cilag, Novartis, Eli Lilly, and Roche, outside the submitted work. MD receives consulting fees from AstraZeneca, Lilly, Roche, Radius, H3 Biomedicine and G1. He also receives honoraria from Nanostring. M.C.U.C. has a patent for Breast Cancer Classifier: US Patent No. 9,631,239 with royalties paid and receive research funding from NanoString Technologies and Veracyte advisory role. And has a patent filed for the novel molecular subgroups identified in this paper. All other authors declare no competing interests. The information in this manuscript is subject to a pending patent application.
Figures




References
-
- Slamon DJ, Clark GM, Wong SG, et al. Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science. 1987;235:177–182. - PubMed
-
- Cejalvo JM, Pascual T, Fernandez-Martinez A, et al. Clinical implications of the non-luminal intrinsic subtypes in hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 2018;67:63–70. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

