METTL3 promotes prostatic hyperplasia by regulating PTEN expression in an m6A-YTHDF2-dependent manner
- PMID: 35985997
- PMCID: PMC9391461
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-022-05162-4
METTL3 promotes prostatic hyperplasia by regulating PTEN expression in an m6A-YTHDF2-dependent manner
Abstract
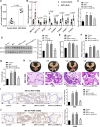
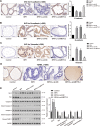
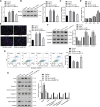
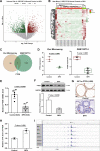
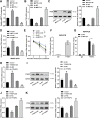
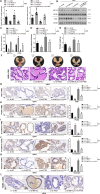
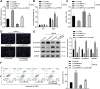
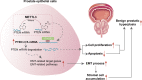
Uncontrolled epithelial cell proliferation in the prostate transition zone and the hyper-accumulation of mesenchymal-like cells derived from the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of prostatic epithelium are two key processes in benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). m6A RNA modification affects multiple cellular processes, including cell proliferation, apoptosis, and differentiation. In this study, the aberrant up-regulation of methylase METTL3 in BPH samples suggests its potential role in BPH development. Elevated m6A modification in the prostate of the BPH rat was partially reduced by METTL3 knockdown. METTL3 knockdown also partially reduced the prostatic epithelial thickness and prostate weight, significantly improved the histological features of the prostate, inhibited epithelial proliferation and EMT, and promoted apoptosis. In vitro, METTL3 knockdown decreased TGF-β-stimulated BPH-1 cell proliferation, m6A modification, and EMT, whereas promoted cell apoptosis. METTL3 increased the m6A modification of PTEN and inhibited its expression through the reading protein YTHDF2. PTEN knockdown aggravated the molecular, cellular, and pathological alterations in the prostate of BPH rats and amplified TGF-β-induced changes in BPH-1 cells. More importantly, PTEN knockdown partially abolished the improving effects of METTL3 knockdown both in vivo and in vitro. In conclusion, the level of m6A modification is elevated in BPH; the METTL3/YTHDF2/PTEN axis disturbs the balance between epithelial proliferation and apoptosis, promotes EMT, and accelerates BPH development in an m6A modification-related manner.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

