Anti-cancer therapeutic strategies based on HGF/MET, EpCAM, and tumor-stromal cross talk
- PMID: 35986321
- PMCID: PMC9389806
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-022-02658-z
Anti-cancer therapeutic strategies based on HGF/MET, EpCAM, and tumor-stromal cross talk
Abstract
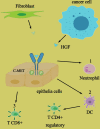
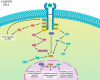
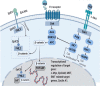
As an intelligent disease, tumors apply several pathways to evade the immune system. It can use alternative routes to bypass intracellular signaling pathways, such as nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB), Wnt, and mitogen-activated protein (MAP)/phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR). Therefore, these mechanisms lead to therapeutic resistance in cancer. Also, these pathways play important roles in the proliferation, survival, migration, and invasion of cells. In most cancers, these signaling pathways are overactivated, caused by mutation, overexpression, etc. Since numerous molecules share these signaling pathways, the identification of key molecules is crucial to achieve favorable consequences in cancer therapy. One of the key molecules is the mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor (MET; c-Met) and its ligand hepatocyte growth factor (HGF). Another molecule is the epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM), which its binding is hemophilic. Although both of them are involved in many physiologic processes (especially in embryonic stages), in some cancers, they are overexpressed on epithelial cells. Since they share intracellular pathways, targeting them simultaneously may inhibit substitute pathways that tumor uses to evade the immune system and resistant to therapeutic agents.
Keywords: EpCAM; HGF/MET; MAP/PI3K/mTOR; NF-κB; Wnt.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of HGF/MET axis in resistance of lung cancer to contemporary management.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2012 Sep;1(3):179-93. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2218-6751.2012.09.04. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 25806180 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activated HGF-c-Met Axis in Head and Neck Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2017 Dec 12;9(12):169. doi: 10.3390/cancers9120169. Cancers (Basel). 2017. PMID: 29231907 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MiR-206 inhibits HGF-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and angiogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer via c-Met /PI3k/Akt/mTOR pathway.Oncotarget. 2016 Apr 5;7(14):18247-61. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7570. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26919096 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiotoxin III suppresses hepatocyte growth factor-stimulated migration and invasion of MDA-MB-231 cells.Cell Biochem Funct. 2014 Aug;32(6):485-95. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3041. Epub 2014 Jun 26. Cell Biochem Funct. 2014. PMID: 24964901
-
Curcumin Inhibits HGF-Induced EMT by Regulating c-MET-Dependent PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathways in Meningioma.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Aug 6;2021:5574555. doi: 10.1155/2021/5574555. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34408780 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The molecular mechanism of NF-κB dysregulation across different subtypes of renal cell carcinoma.J Adv Res. 2025 Jun;72:501-514. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.07.030. Epub 2024 Jul 31. J Adv Res. 2025. PMID: 39094893 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential biomarkers of aortic dissection based on expression network analysis.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2023 Mar 23;23(1):147. doi: 10.1186/s12872-023-03173-3. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2023. PMID: 36959563 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting c-Met in Cancer Therapy: Unravelling Structure-activity Relationships and Docking Insights for Enhanced Anticancer Drug Design.Curr Top Med Chem. 2025;25(4):409-433. doi: 10.2174/0115680266331025241015084546. Curr Top Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 39484763 Review.
-
Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes for treatment of solid tumors: It takes two to tango?Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 28;13:1018962. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1018962. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36389779 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lenvatinib resistance mechanism and potential ways to conquer.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Apr 20;14:1153991. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1153991. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37153782 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Trusolino L, Comoglio PM. Scatter-factor and semaphorin receptors: cell signalling for invasive growth. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2(4):289–300. - PubMed
-
- Schmidt L, Duh F-M, Chen F, Kishida T, Glenn G, Choyke P, et al. Germline and somatic mutations in the tyrosine kinase domain of the MET proto-oncogene in papillary renal carcinomas. Nat Genet. 1997;16(1):68–73. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

