IL1RAP expression and the enrichment of IL-33 activation signatures in severe neutrophilic asthma
- PMID: 35986608
- PMCID: PMC10086999
- DOI: 10.1111/all.15487
IL1RAP expression and the enrichment of IL-33 activation signatures in severe neutrophilic asthma
Abstract
Background: Interleukin (IL)-33 is an upstream regulator of type 2 (T2) eosinophilic inflammation and has been proposed as a key driver of some asthma phenotypes.
Objective: To derive gene signatures from in vitro studies of IL-33-stimulated cells and use these to determine IL-33-associated enrichment patterns in asthma.
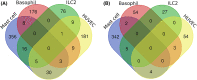
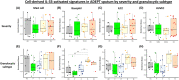
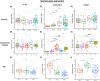
Methods: Signatures downstream of IL-33 stimulation were derived from our in vitro study of human mast cells and from public datasets of in vitro stimulated human basophils, type 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2), regulatory T cells (Treg) and endothelial cells. Gene Set Variation Analysis (GSVA) was used to probe U-BIOPRED and ADEPT sputum transcriptomics to determine enrichment scores (ES) for each signature according to asthma severity, sputum granulocyte status and previously defined molecular phenotypes.
Results: IL-33-activated gene signatures were cell-specific with little gene overlap. Individual signatures, however, were associated with similar signalling pathways (TNF, NF-κB, IL-17 and JAK/STAT signalling) and immune cell differentiation pathways (Th17, Th1 and Th2 differentiation). ES for IL-33-activated gene signatures were significantly enriched in asthmatic sputum, particularly in patients with neutrophilic and mixed granulocytic phenotypes. IL-33 mRNA expression was not elevated in asthma whereas the expression of mRNA for IL1RL1, the IL-33 receptor, was up-regulated in the sputum of severe eosinophilic asthma. The mRNA expression for IL1RAP, the IL1RL1 co-receptor, was greatest in severe neutrophilic and mixed granulocytic asthma.
Conclusions: IL-33-activated gene signatures are elevated in neutrophilic and mixed granulocytic asthma corresponding with IL1RAP co-receptor expression. This suggests incorporating T2-low asthma in anti-IL-33 trials.
Keywords: IL-33; gene set variation analysis; severe asthma.
© 2022 The Authors. Allergy published by European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Adam Taylor, John H Riley, Sally Worsley, Karen Affleck and Stewart Bates have worked or are currently working for GSK. Batika Rana is currently working for Orchard Therapeutics and Yusef Eamon Badi is currently working at BenevolentAI. MN, Silvia Bulfone‐Paus, Kian Fan Chung, DJC and IMA have received investigator‐led research grants from GSK. YB and Barbora Salcman are supported by BBSRC CASE awards. DJC has received investigator‐led research grants from AstraZeneca and Genentech. There are no other conflicts of interest regarding this manuscript.
Figures



References
-
- Komai‐Koma M, Xu D, Li Y, McKenzie AN, McInnes IB, Liew FY. IL‐33 is a chemoattractant for human Th2 cells. Eur J Immunol. 2007;37:2779‐2786. 2710.1002/eji.200737547. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

