Hexavalent chromium elimination from wastewater by integrated micro-electrolysis composites synthesized from red mud and rice straw via a facile one-pot method
- PMID: 35987789
- PMCID: PMC9392804
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-18598-7
Hexavalent chromium elimination from wastewater by integrated micro-electrolysis composites synthesized from red mud and rice straw via a facile one-pot method
Abstract
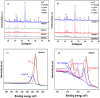
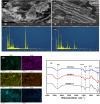
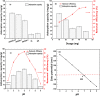
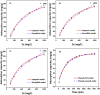
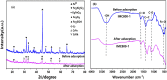
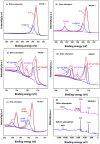
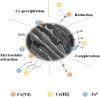
The widely spread chromium (Cr) contamination is rising environmental concerns, while the reutilization of agro-industrial by-products are also urgently demanded due to their potential risks. In this study, we prepared the integrated micro-electrolysis composites (IMC) through a facile one-pot method with red mud and rice straw. The effects of components relatively mass ratios as well as pyrolysis temperature were analyzed. The XRD, XPS, SEM, FTIR, and various techniques proved the IMC was successfully synthesized, which was also used to analyze the reaction mechanisms. In this study, the dosage of IMC, pH, adsorption time, and temperature of adsorption processes were explored, in the adsorption experiment of Cr(VI), dosage of IMC was 2 g/L (pH 6, 25 °C, and 200 rpm) for isothermal, while the concentration and contact time were also varied. According to the batch experiments, IMC exhibited acceptable removal capacity (190.6 mg/g) on Cr(VI) and the efficiency reached 97.74%. The removal mechanisms of adsorbed Cr(VI) were mainly elaborated as chemical reduction, complexation, co-precipitation, and physical adherence. All these results shed light on the facile preparation and agro-industrial by-products recycled as engineering materials for the heavy metals decontamination in wastewater.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Zhou X, et al. Tunable S doping from Co3O4 to Co9S8 for peroxymonosulfate activation: Distinguished Radical/Nonradical species and generation pathways. Appl. Catal. B. 2021;282:119605. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119605. - DOI
-
- Hong Y, et al. Efficient degradation of atrazine by CoMgAl layered double oxides catalyzed peroxymonosulfate: Optimization, degradation pathways and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2019;370:354–363. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.03.127. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

