Low Xanthophylls, Retinol, Lycopene, and Tocopherols in Grey and White Matter of Brains with Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 35988225
- PMCID: PMC10357197
- DOI: 10.3233/JAD-220460
Low Xanthophylls, Retinol, Lycopene, and Tocopherols in Grey and White Matter of Brains with Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
Background: Oxidative stress contributes to pathogenesis and progression of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Higher levels of the dietary antioxidants- carotenoids and tocopherols- are associated with better cognitive functions and lower risk for AD, and lower levels of multiple carotenoids are found in serum and plasma of patients with AD. Although brains donated by individuals with mild cognitive impairment had significantly lower levels of lutein and beta-carotene, previous investigators found no significant difference in carotenoid levels of brains with AD and cognitively normal brains.
Objective: This study tested the hypothesis that micronutrients are significantly lower in donor brains with AD than in healthy elderly brains.
Methods: Samples of donor brains with confirmed AD or verified health were dissected into grey and white matter, extracted with organic solvents and analyzed by HPLC.
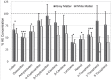
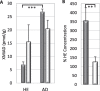
Results: AD brains had significantly lower levels of lutein, zeaxanthin, anhydrolutein, retinol, lycopene, and alpha-tocopherol, and significantly increased levels of XMiAD, an unidentified xanthophyll metabolite. No meso-zeaxanthin was detected. The overlapping protective roles of xanthophylls, carotenes, α- and γ-tocopherol are discussed.
Conclusion: Brains with AD had substantially lower concentrations of some, but not all, xanthophylls, carotenes, and tocopherols, and several-fold higher concentrations of an unidentified xanthophyll metabolite increased in AD (XMiAD).
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; antioxidants; brain; carotenoids; deficiency; lutein; lycopene; meso-zeaxanthin; oxidation; tocopherols; zeaxanthin.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors’ disclosures available online (
Figures




Similar articles
-
Carotenoid, tocopherol, and retinol concentrations in elderly human brain.J Nutr Health Aging. 2004;8(3):156-62. J Nutr Health Aging. 2004. PMID: 15129301
-
Exploratory 5-year follow-up study of retinol, tocopherols, and carotenoids in multiple sclerosis.Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2024 Jan;81:105143. doi: 10.1016/j.msard.2023.105143. Epub 2023 Nov 25. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2024. PMID: 38039941
-
A European multicentre, placebo-controlled supplementation study with alpha-tocopherol, carotene-rich palm oil, lutein or lycopene: analysis of serum responses.Clin Sci (Lond). 2002 Apr;102(4):447-56. Clin Sci (Lond). 2002. PMID: 11914107 Clinical Trial.
-
The Associations of Plasma/Serum Carotenoids with Alzheimer's Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Alzheimers Dis. 2021;82(3):1055-1066. doi: 10.3233/JAD-210384. J Alzheimers Dis. 2021. PMID: 34151808
-
Non-nutritive bioactive constituents of plants: lycopene, lutein and zeaxanthin.Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 2003 Mar;73(2):95-100. doi: 10.1024/0300-9831.73.2.95. Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 2003. PMID: 12747216 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects and Mechanisms of Lutein on Aging and Age-Related Diseases.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Sep 14;13(9):1114. doi: 10.3390/antiox13091114. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39334773 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential responses of primary neuron-secreted MCP-1 and IL-9 to type 2 diabetes and Alzheimer's disease-associated metabolites.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 3;14(1):12743. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-62155-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38830911 Free PMC article.
-
The role of α-tocopherol in the prevention and treatment of Alzheimer's disease.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 Jun;480(6):3385-3398. doi: 10.1007/s11010-025-05214-1. Epub 2025 Jan 20. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 39832109 Review.
-
Association of dietary and nutritional factors with cognitive decline, dementia, and depressive symptomatology in older individuals according to a neurogenesis-centred biological susceptibility to brain ageing.Age Ageing. 2024 May 11;53(Suppl 2):ii47-ii59. doi: 10.1093/ageing/afae042. Age Ageing. 2024. PMID: 38745492 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial: Feast your eyes: diet and nutrition for optimal eye health.Front Nutr. 2025 Mar 4;12:1579901. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1579901. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40104816 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- (2020) 2020 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement 113, 200–208. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization, Dementia, https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dementia, Accessed March 21, 2022.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

