Neuromodulation therapy for atrial fibrillation
- PMID: 35988908
- PMCID: PMC10224761
- DOI: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2022.08.011
Neuromodulation therapy for atrial fibrillation
Abstract
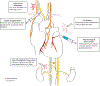
Atrial fibrillation has a multifactorial pathophysiology influenced by cardiac autonomic innervation. Both sympathetic and parasympathetic influences are profibrillatory. Innovative therapies targeting the neurocardiac axis include catheter ablation or pharmacologic suppression of ganglionated plexi, renal sympathetic denervation, low-level vagal stimulation, and stellate ganglion blockade. To date, these therapies have variable efficacy. As our understanding of atrial fibrillation and the cardiac nervous system expands, our approach to therapeutic neuromodulation will continue evolving for the benefit of those with AF.
Keywords: Atrial fibrillation; Autonomics; Ganglionated plexi; Neurocardiac axis; Neuromodulation.
Copyright © 2022 Heart Rhythm Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Bhatt HV, Fischer GW. Atrial Fibrillation: Pathophysiology and Therapeutic Options. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth 2015;29:1333–1340. - PubMed
-
- de Vos CB, Nieuwlaat R, Crijns HJGM, et al. Autonomic trigger patterns and anti-arrhythmic treatment of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. EHJ 2008;29:632–639. - PubMed
-
- January CT, Wann LS, Alpert JS, et al. 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS Guideline for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation. JACC 2014;64:e1–e76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

