Modified cardiovascular SOFA score in sepsis: development and internal and external validation
- PMID: 35989336
- PMCID: PMC9394016
- DOI: 10.1186/s12916-022-02461-7
Modified cardiovascular SOFA score in sepsis: development and internal and external validation
Erratum in
-
Correction: Modified cardiovascular SOFA score in sepsis: development and internal and external validation.BMC Med. 2022 Dec 8;20(1):476. doi: 10.1186/s12916-022-02694-6. BMC Med. 2022. PMID: 36482459 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: The Sepsis-3 criteria introduced the system that uses the Sequential Organ-Failure Assessment (SOFA) score to define sepsis. The cardiovascular SOFA (CV SOFA) scoring system needs modification due to the change in guideline-recommended vasopressors. In this study, we aimed to develop and to validate the modified CV SOFA score.
Methods: We developed, internally validated, and externally validated the modified CV SOFA score using the suspected infection cohort, sepsis cohort, and septic shock cohort. The primary outcome was 28-day mortality. The modified CV SOFA score system was constructed with consideration of the recently recommended use of the vasopressor norepinephrine with or without lactate level. The predictive validity of the modified SOFA score was evaluated by the discrimination for the primary outcome. Discrimination was assessed using the area under the receiver operating characteristics curve (AUC). Calibration was assessed using the calibration curve. We compared the prognostic performance of the original CV/total SOFA score and the modified CV/total SOFA score to detect mortality in patients with suspected infection, sepsis, or septic shock.
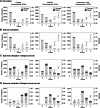
Results: We identified 7,393 patients in the suspected cohort, 4038 patients in the sepsis cohort, and 3,107 patients in the septic shock cohort in seven Korean emergency departments (EDs). The 28-day mortality rates were 7.9%, 21.4%, and 20.5%, respectively, in the suspected infection, sepsis, and septic shock cohorts. The model performance is higher when vasopressor and lactate were used in combination than the vasopressor only used model. The modified CV/total SOFA score was well-developed and internally and externally validated in terms of discrimination and calibration. Predictive validity of the modified CV SOFA was significantly higher than that of the original CV SOFA in the development set (0.682 vs 0.624, p < 0.001), test set (0.716 vs 0.638), and all other cohorts (0.648 vs 0.557, 0.674 vs 0.589). Calibration was modest. In the suspected infection cohort, the modified model classified more patients to sepsis (66.0 vs 62.5%) and identified more patients at risk of septic mortality than the SOFA score (92.6 vs 89.5%).
Conclusions: Among ED patients with suspected infection, sepsis, and septic shock, the newly-developed modified CV/total SOFA score had higher predictive validity and identified more patients at risk of septic mortality.
Keywords: Mortality; Organ dysfunction scores; Sepsis; Severity of illness index.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Rudd KE, Johnson SC, Agesa KM, Shackelford KA, Tsoi D, Kievlan DR, Colombara DV, Ikuta KS, Kissoon N, Finfer S, et al. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990–2017: analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet. 2020;395(10219):200–211. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32989-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vincent JL, Moreno R, Takala J, Willatts S, De Mendonca A, Bruining H, Reinhart CK, Suter PM, Thijs LG. The SOFA (Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment) score to describe organ dysfunction/failure. On behalf of the Working Group on Sepsis-Related Problems of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Intensive Care Med. 1996;22(7):707–710. doi: 10.1007/BF01709751. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

