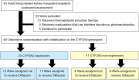
The effect of the very low dosage diltiazem on tacrolimus exposure very early after kidney transplantation: a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 35989346
- PMCID: PMC9393165
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-18552-7
The effect of the very low dosage diltiazem on tacrolimus exposure very early after kidney transplantation: a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
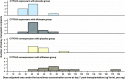
The objective of this study was to assess the effect of the very low dosage of diltiazem on tacrolimus exposure during the first week post-kidney transplantation, among cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A5 expressers who did not receive diltiazem (EXplb), CYP3A5 expressers who received the very low dose diltiazem (EXdtz), CYP3A5 nonexpressers who did not receive diltiazem (NEplb), and CYP3A5 nonexpressers who received the very low dose diltiazem (NEdtz). Forty kidney recipients who receive tacrolimus-based immunosuppressive regimen were randomly assigned, with stratification on the CYP3A5 genotypes, to receive either diltiazem 30 mg every 12 h or a matched placebo. The observed median dose-adjusted area under the 12-h curve of tacrolimus concentration (AUC/D) at day 7 post-transplantation was lowest in the EXplb group followed by EXdtz, NEplb, and NEdtz at 34.9, 43.6, 49.4, and 71.1 ng*h/mL per mg, respectively. A Kruskal-Wallis test showed a significant difference in the mean ranks of AUC/D among groups. Significant differences between EXplb and NEplb, and between EXplb and NEdtz were demonstrated, whereas no sufficient evidence of significant differences was detected between the other pairs. In conclusion, coadministration of diltiazem 30 mg twice daily may be advantageous for increasing tacrolimus exposure early after kidney transplantation among CYP3A5 expressers.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical