The liver cancer immune microenvironment: Therapeutic implications for hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 35989535
- PMCID: PMC9941399
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.32740
The liver cancer immune microenvironment: Therapeutic implications for hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
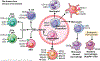
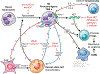
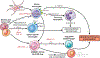
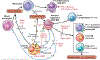
The liver is the sixth most common site of primary cancer in humans and the fourth leading cause of cancer-related death in the world. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) accounts for 90% of liver cancers. HCC is a prevalent disease with a progression that is modulated by the immune system. Half of the patients with HCC receive systemic therapies, traditionally sorafenib or lenvatinib, as a first-line therapy. In the last few years, immune-checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have revolutionized cancer therapy and have gained an increased interest in the treatment of HCC. In 2020, the combination of atezolizumab (anti-programmed death-ligand 1) and bevacizumab (anti-vascular endothelial growth factor) improved overall survival over sorafenib, resulting in Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval as a first-line treatment for patients with advanced HCC. Despite these major advances, a better molecular and cellular characterization of the tumor microenvironment is still needed because it has a crucial role in the development and progression of HCC. Inflamed (hot) and noninflamed (cold) HCC tumors and genomic signatures have been associated with response to ICIs. However, there are no additional biomarkers to guide clinical decision-making. Other immune-targeting strategies, such as adoptive T-cell transfer, vaccination, and virotherapy, are currently under development. This review provides an overview on the HCC immune microenvironment, different cellular players, current available immunotherapies, and potential immunotherapy modalities.
Copyright © 2023 American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
A.L. has received research funding from Pfizer and Genentech, and has received a consulting fee from Astra Zeneca.
Figures
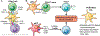
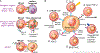
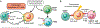

References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians 2021;71:209–249. - PubMed
-
- Wittekind C [Pathology of liver tumors]. Zentralbl Chir 2000;125:587–591. - PubMed
-
- Global Burden of Disease Liver Cancer Collaboration, Akinyemiju T, Abera S, Ahmed M, Alam N, Alemayohu MA, et al. The Burden of Primary Liver Cancer and Underlying Etiologies From 1990 to 2015 at the Global, Regional, and National Level: Results From the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. JAMA Oncol 2017;3:1683–1691. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sanyal A, Poklepovic A, Moyneur E, Barghout V. Population-based risk factors and resource utilization for HCC: US perspective. Curr Med Res Opin 2010;26:2183–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

