Regulation of the pyrimidine biosynthetic pathway by lysine acetylation of E. coli OPRTase
- PMID: 35989594
- PMCID: PMC10087573
- DOI: 10.1111/febs.16598
Regulation of the pyrimidine biosynthetic pathway by lysine acetylation of E. coli OPRTase
Abstract
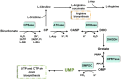
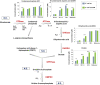
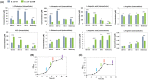
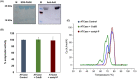
The de novo pyrimidine biosynthesis pathway is an important route due to the relevance of its products, its implications in health and its conservation among organisms. Here, we investigated the regulation by lysine acetylation of this pathway. To this aim, intracellular and extracellular metabolites of the route were quantified, revealing a possible blockage of the pathway by acetylation of the OPRTase enzyme (orotate phosphoribosyltransferase). Chemical acetylation of OPRTase by acetyl-P involved a decrease in enzymatic activity. To test the effect of acetylation in this enzyme, K26 and K103 residues were selected to generate site-specific acetylated proteins. Several differences were observed in kinetic parameters, emphasizing that the kcat of these mutants showed a strong decrease of 300 and 150-fold for OPRTase-103AcK and 19 and 6.3-fold for OPRTase-26AcK, for forward and reverse reactions. In vivo studies suggested acetylation of this enzyme by a nonenzymatic acetyl-P-dependent mechanism and a reversion of this process by the CobB deacetylase. A complementation assay of a deficient strain in the pyrE gene with OPRTase-26AcK and OPRTase-103AcK was performed, and curli formation, stoichiometric parameters and orotate excretion were measured. Complementation with acetylated enzymes entailed a profile very similar to that of the ∆pyrE strain, especially in the case of complementation with OPRTase-103AcK. These results suggest regulation of the de novo pyrimidine biosynthesis pathway by lysine acetylation of OPRTase in Escherichia coli. This finding is of great relevance due to the essential role of this route and the OPRTase enzyme as a target for antimicrobial, antiviral and cancer treatments.
Keywords: E. coli; OPRTase; lysine acetylation; pyrimidine biosynthesis pathway; regulation.
© 2022 The Authors. The FEBS Journal published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Interallelic complementation at the pyrF locus and the homodimeric nature of orotate phosphoribosyltransferase (OPRTase) in Mucor circinelloides.Mol Gen Genet. 1998 Nov;260(2-3):251-60. doi: 10.1007/s004380050893. Mol Gen Genet. 1998. PMID: 9862479
-
Heterospecific cloning of Arabidopsis thaliana cDNAs by direct complementation of pyrimidine auxotrophic mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. I. Cloning and sequence analysis of two cDNAs catalysing the second, fifth and sixth steps of the de novo pyrimidine biosynthesis pathway.Mol Gen Genet. 1994 Jul 8;244(1):23-32. doi: 10.1007/BF00280183. Mol Gen Genet. 1994. PMID: 8041358
-
Orotate phosphoribosyltransferase from yeast: studies of the structure of the pyrimidine substrate binding site.Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Aug 1;272(2):421-32. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90236-1. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989. PMID: 2665650
-
Orotate phosphoribosyltransferase from Thermus thermophilus: overexpression in Escherichia coli, purification and characterization.J Biochem. 1995 Dec;118(6):1261-7. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a125016. J Biochem. 1995. PMID: 8720144
-
Orotate phosphoribosyltransferase from Corynebacterium ammoniagenes lacking a conserved lysine.J Bacteriol. 2007 Dec;189(24):9030-6. doi: 10.1128/JB.01161-07. Epub 2007 Oct 5. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17921291 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Mapping protein-metabolite interactions in E. coli by integrating chromatographic techniques and co-fractionation mass spectrometry.iScience. 2025 May 8;28(6):112611. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.112611. eCollection 2025 Jun 20. iScience. 2025. PMID: 40491478 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zrenner R, Stitt M, Sonnewald U, Boldt R. Pyrimidine and purine biosynthesis and degradation in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2006;57:805–36. - PubMed
-
- Jones ME. Pyrimidine nucleotide biosynthesis in animals: genes, enzymes and regulation of UMP biosynthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:253–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

