The silent crisis of child abuse in the COVID-19 pandemic: A scoping review
- PMID: 35989944
- PMCID: PMC9386128
- DOI: 10.1002/hsr2.790
The silent crisis of child abuse in the COVID-19 pandemic: A scoping review
Abstract
Background and aims: The global outbreak of COVID-19 has become an international concern. The lives of children are severely affected by COVID-19 pandemic. There is evidence of a pandemic impact on violence against children. This scoping review study aimed to investigate the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on child abuse.
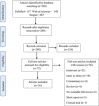
Methods: We searched PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science databases to retrieve related studies. Regarding the recent incident of COVID-19, the articles were reviewed from 2019 to June 1, 2021. The terms Child abuse and COVID-19 were used in the precise search technique of each database. The search techniques were created to work with any scientific database that used the keywords given.
Results: In the initial search of scientific databases, 568 articles were retrieved. After applying the inclusion and exclusion criteria during the screening process, 16 papers were included in the scoping review. Twelve articles have mentioned the increase of physical, psychological, and neglect types of abuse. However, sexual violence has not been reported in any of the articles. Four articles reported a reduction in the incidence of child abuse.
Conclusion: During the COVID-19 pandemic, a crisis occurred in the form of an upsurge in violence toward children, since limits made to diminish the virus, in general, increased the danger to children. Numerous factors such as stress, poverty, financial situation, history of violence, school closures, and lack of contact with support organizations contribute to this phenomenon. Social action and support needed is the right of every child in need in this critical situation.
Keywords: COVID‐19; child abuse; child maltreatment; violence.
© 2022 The Authors. Health Science Reports published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). Coronavirus Disease (COVID‐19) Pandemic. Accessed May 3, 2021. https://www.euro.who.int/en/health-topics/health-emergencies/coronavirus...
-
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID‐19): Situation Report; 2020:94.
-
- Wu Z, McGoogan JM. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese center for disease control and prevention. JAMA. 2020;323(13):1239‐1242. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . Coronavirus Disease (COVID‐19). Accessed June 2, 2022. https://www.who.int/health-topics/coronavirus#tab=tab_1
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources