Dynamic Evaluation of Transformation Ability for Emergency Scientific Research Achievements Based on an Improved Minimum Distance-Maximum Entropy Combination Weighting Method: A Case Study of COVID-19 Epidemic Data
- PMID: 35990119
- PMCID: PMC9391140
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/8005249
Dynamic Evaluation of Transformation Ability for Emergency Scientific Research Achievements Based on an Improved Minimum Distance-Maximum Entropy Combination Weighting Method: A Case Study of COVID-19 Epidemic Data
Abstract
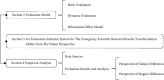
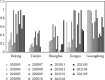
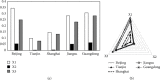
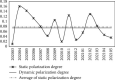
In the process of responding to major public health emergencies, the transformation of emergency scientific research results often faces many unfavourable factors such as limited resources, tight time, changes in needs, and lack of results. It is necessary to evaluate and analyze the ability to transform emergency scientific research results under public health emergencies, so as to rationally allocate emergency scientific research resources between subjects and regions, improve the efficiency of emergency results transformation, enhance emergency scientific research capabilities, and efficiently support incident prevention, control, and treatment. Starting from the patent level, this paper constructs an indicator system to evaluate the transformation ability of emergency scientific research results under major public health emergencies. It improves the minimum distance-maximum entropy combination weighting method to realize the static evaluation of transformation ability for emergency scientific research results from the perspective of patents, then constructs the dynamic evaluation model of transformation ability for emergency scientific research results in public health emergencies from the perspective of patents, and carries out the dynamic evaluation of the emergency scientific research achievements transformation ability of different subjects and different regions. We also improve the ER index, measure the static polarization effect of the transformation ability for regional emergency scientific research results, and consider the time factor to construct a dynamic polarization effect measurement model for the transformation ability of emergency scientific research achievement. Furthermore, this paper improves the measurement model of contribution degree to the polarization effect, and analyzes the contribution degree to polarization of the transformation ability for regional emergency scientific research results.
Copyright © 2022 Qingmei Tan and Juan Hui.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest in this manuscript.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Dynamic changes and improvement paths of China's emergency logistics response capabilities under public emergencies-research based on the entropy weight TOPSIS method.Front Public Health. 2024 Jul 10;12:1397747. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1397747. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39050606 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring time evolution characteristics of the collaborative mode in emergency information release of public health emergencies: A network analysis of response to COVID-19 from the central government of China.Front Public Health. 2022 Aug 29;10:970514. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.970514. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36106165 Free PMC article.
-
Research on the evaluation of emergency management capability for urban public health emergencies under the perspective of resilience-a case study of Henan Province, China.Front Public Health. 2024 Nov 4;12:1431158. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1431158. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39559375 Free PMC article.
-
Research on the collaborative evolution process of information in public health emergencies based on complex adaptive system theory and social network analysis: a case study of the COVID-19 pandemic.Front Public Health. 2023 Sep 25;11:1210255. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1210255. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37818306 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Status and Challenges of Public Health Emergency Management in China Related to COVID-19.Front Public Health. 2020 May 29;8:250. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2020.00250. eCollection 2020. Front Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32574311 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Liu Y., Lee J. M., Lee C. The challenges and opportunities of a global health crisis: the management and business implications of COVID-19 from an Asian perspective. Asian Business & Management . 2020;19(3):277–297. doi: 10.1057/s41291-020-00119-x. - DOI
-
- Gibson C. Guidepost from ‘social distancing’to ‘care in connecting’: an emerging organizational research agenda for turbulent times. Academy of Management Discoveries . 2020;6(2):200–212. doi: 10.5465/amd.2020.0062. - DOI
-
- León-Sandoval E., Zareei M., Barbosa-Santillán L. I., Falcón Morales L. E., Pareja Lora A., Ochoa Ruiz G. Monitoring the emotional response to the covid-19 pandemic using sentiment analysis: a case study in Mexico. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience . 2022;2022:11. doi: 10.1155/2022/4914665.4914665 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

